Obtain a postprocedural CT scan of the head as early as possible to check the status of the hematoma. Donovan DJ, Moquin RR, Ecklund JM. Is CT Scanning Necessary in Patients with Tentorial Herniation? The parietal or posterior burr hole is made two finger breadths behind the external auditory meatus and three finger breadths above the mastoid process (Figure 116-7B). The one I ordered arrived the day before a 2-year-old patient arrived at triage. Typical locations for burr holes. The tip of the perforator bit is designed to penetrate the inner table of the skull and lock without allowing it to puncture the dura or the brain (Figure 116-6). focus These may require reversal with the administration of fresh frozen plasma and/or platelets.  This is when blood slowly builds up under the dura layerafter a mild head injury. Temporising an extradural haematoma by intraosseous needle craniostomy in the District General Hospital by non-neurosurgical doctors A case report. Turn the head to the contralateral side if the cervical spine has been cleared. Smith SW, Clark M, Nelson J, et al.
This is when blood slowly builds up under the dura layerafter a mild head injury. Temporising an extradural haematoma by intraosseous needle craniostomy in the District General Hospital by non-neurosurgical doctors A case report. Turn the head to the contralateral side if the cervical spine has been cleared. Smith SW, Clark M, Nelson J, et al.  The bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes (Figure 116-5). Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy. Enter your email address to receive notifications of new posts by email. a) indicators of transtentorial herniation/brainstem compression: sudden drop in Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, paralysis or decerebration develops (usually contralateral to blown pupil). Always maintain the drill perpendicular to the skull. seong soonchunhyang maximal burr indications versus Your email address will not be published. I had seen one of these in residency and went to the supply room to find the newly arrived burr hole kit, took a deep breath, then started to prepare for the procedure by reviewing the CT.
The bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes (Figure 116-5). Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy. Enter your email address to receive notifications of new posts by email. a) indicators of transtentorial herniation/brainstem compression: sudden drop in Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, paralysis or decerebration develops (usually contralateral to blown pupil). Always maintain the drill perpendicular to the skull. seong soonchunhyang maximal burr indications versus Your email address will not be published. I had seen one of these in residency and went to the supply room to find the newly arrived burr hole kit, took a deep breath, then started to prepare for the procedure by reviewing the CT.
The veins there are fragile and easy to break, especially in older adults. However, if the burr hole is positive, it is possible that modest decompression may be performed, and then the definitive craniotomy can be undertaken incorporating the burr hole(s). articular beneath bereiter indications (equipped to handle craniotomy, better lighting and sterility, dedicated scrub nurse) especially in older patients (>30 yrs) not involved in MVAs. Other contraindications include localized infections of the scalp and patients who are thrombocytopenic. CT scanning also verifies catheter location and reduction in ventricular size in patients in which trephination has been completed for ventricular catheter placement. https://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=683§ionid=45343759. The below instructions are for a temporal ICH (intracranial hematoma epidural/subdural), which is the most common ICH. The clot of an epidural hematoma will be obvious as it separates the inner table of the skull from the dura. This makes it more vulnerable to a fracture with an associated injury to the underlying middle meningeal vessels. The general steps include 4: After this operation, youll move to the recovery place and stay in the hospital for 1 or 2 days. The prognosis for the severely head-injured patient with clinical evidence of tentorial herniation and brainstem compression is poor. Perform a time out to ensure that everyone involved is aware of the patient identity, the plan for the coming procedure, why the procedure is being performed, and the side on which the procedure will occur.
Examples of perforator bits (left) and burr bits (right). 2007, 21 (1): 11-15. Turn the crank slowly and smoothly, while continuing to apply pressure. A 53-year-old female with no significant past medical history presents to the Emergency Department (ED) with headache after syncope while on a treadmill. The distal end has a snap lock chuck that slides to allow easy insertion and removal of the bits. Confirm skull thickness on CT as seen below in figure 1. You elevate the head of the bed and start IV antihypertensives. Fit the Hudson brace drill with a perforator bit. Notify me of follow-up comments by email. SDH was the most common extraaxial mass lesion (alone and unilateral in 70%, bilateral in 1 1 %, and in combination with EDH or ICH in > 9 %) . Check often for the bone fragment in the instrument. Another option is to obtain a lateral plain radiograph of the skull. Prophylactic intravenous antibiotic coverage is recommended if time permits. The frontal burr hole can be used to drain an intracranial hematoma or to perform a ventriculostomy. trauma, 4. if no localizing clues, place hole on left side (to evaluate and decompress the dominant Cranioplasty is often not completed initially after burr hole placement in order to minimize the infectious risk. exploratory burr holes (bilateral temporal, frontal and parietal, done in the O.R.) Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Use a small sterile pediatric suction catheter to facilitate hematoma drainage. A head CT revealed a large epidural hematoma with midline shift.
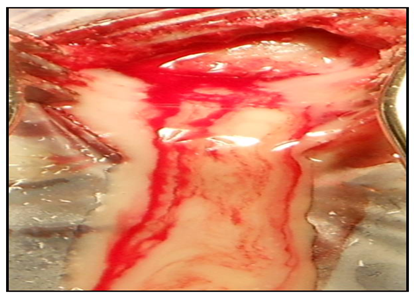 Its sounds just like one of those scenes from those medical dramas. After intubation what are your next steps? An error has occurred sending your email(s). B. CT scan of an epidural hematoma. Infiltrate 5 mL of lidocaine containing epinephrine along the proposed incision site and down to the level of the periosteum on the skull. A large area of the temporal region is shaved and prepared in a sterile manner with betadine/chlorhexidine and a local anesthetic injected subcutaneously using a 25G needle. Like other surgical operations, burr hole surgery comprises some risks during and after operation. Hemostasis can often be obtained with the use of the retractor. This includes pupillary dilation with a decreased or absent light reflex, progressive deterioration in the patient's level of consciousness, and/or hemiparesis including posturing (decerebrate/decorticate) or flaccidity. Wilson, M.H., Wise, D., Davies, G. et al. Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may extrude spontaneously or require gentle suction with a catheter. Have an assistant hold the patients head firmly prior to drilling. The risk of surgical complications is even higher in this area; therefore, it should be pursued only as a last resort or if there is obvious injury only to this area.8, Your email address will not be published. bifrontal craniotomy supraorbital The surgeon will make a cut (incision) in your scalp. Rotate the handle clockwise to enlarge the hole in the skull (Figure 116-8D). During the conversation with the trauma surgeon at the major academic center, I told him I was planning on doing an emergent burr hole. However, when they do occur, they signify cerebral compression and transtentorial herniation. This builds up of blood eventually can lead to death while left untreated. I ordered the necessary kits so we would have the tools on-site. Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license:CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International. Controversial. Remove the perforator bit from the Hudson brace drill. Durnford S, Bulstrode H, Durnford A, Chakraborty A, Tarmey NT. Extradural Hematoma: Observations on 125 Cases. Finally, your surgeon will close this hole or left it open with a drain or shunt attached. Wellcome Images/Science Source, Topics: Burr HoleCase ReportsCritical CareEmergency DepartmentEmergency MedicineEmergency Physicianshead injuryPatient CareTrauma and InjuryTrephination. Hold the Hudson brace drill as described above. Prophylactic antibiotics covering gram positive organisms should be considered at this time. 120-122. Accessibility
undergoing transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression as outlined above, Emergency department skull trephinations are done in the temporal location 2 cm anterior and 2 cm superior to the tragus.1, Trephinations of the skull have been found in human skulls older than 10,000 years of age. My partner drilled on an elderly man comatose with herniating SDH. Suspect a space-occupying lesion when there is clinical evidence of tentorial herniation or upper brain stem dysfunction.
Its sounds just like one of those scenes from those medical dramas. After intubation what are your next steps? An error has occurred sending your email(s). B. CT scan of an epidural hematoma. Infiltrate 5 mL of lidocaine containing epinephrine along the proposed incision site and down to the level of the periosteum on the skull. A large area of the temporal region is shaved and prepared in a sterile manner with betadine/chlorhexidine and a local anesthetic injected subcutaneously using a 25G needle. Like other surgical operations, burr hole surgery comprises some risks during and after operation. Hemostasis can often be obtained with the use of the retractor. This includes pupillary dilation with a decreased or absent light reflex, progressive deterioration in the patient's level of consciousness, and/or hemiparesis including posturing (decerebrate/decorticate) or flaccidity. Wilson, M.H., Wise, D., Davies, G. et al. Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may extrude spontaneously or require gentle suction with a catheter. Have an assistant hold the patients head firmly prior to drilling. The risk of surgical complications is even higher in this area; therefore, it should be pursued only as a last resort or if there is obvious injury only to this area.8, Your email address will not be published. bifrontal craniotomy supraorbital The surgeon will make a cut (incision) in your scalp. Rotate the handle clockwise to enlarge the hole in the skull (Figure 116-8D). During the conversation with the trauma surgeon at the major academic center, I told him I was planning on doing an emergent burr hole. However, when they do occur, they signify cerebral compression and transtentorial herniation. This builds up of blood eventually can lead to death while left untreated. I ordered the necessary kits so we would have the tools on-site. Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license:CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International. Controversial. Remove the perforator bit from the Hudson brace drill. Durnford S, Bulstrode H, Durnford A, Chakraborty A, Tarmey NT. Extradural Hematoma: Observations on 125 Cases. Finally, your surgeon will close this hole or left it open with a drain or shunt attached. Wellcome Images/Science Source, Topics: Burr HoleCase ReportsCritical CareEmergency DepartmentEmergency MedicineEmergency Physicianshead injuryPatient CareTrauma and InjuryTrephination. Hold the Hudson brace drill as described above. Prophylactic antibiotics covering gram positive organisms should be considered at this time. 120-122. Accessibility
undergoing transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression as outlined above, Emergency department skull trephinations are done in the temporal location 2 cm anterior and 2 cm superior to the tragus.1, Trephinations of the skull have been found in human skulls older than 10,000 years of age. My partner drilled on an elderly man comatose with herniating SDH. Suspect a space-occupying lesion when there is clinical evidence of tentorial herniation or upper brain stem dysfunction.
Position patient in supination and elevate the shoulder ipsilateral to the ICH with a shoulder roll. Place the burr bit into the hole in the skull. The coronal suture is often palpable. When burr holes were positive, the first burr hole was on the correct side 86% of the time when placed as suggested above. Mahoney BD, Rockswold GL, Ruiz E, Clinton JE. Irrigate the area. Contact us at [emailprotected]. You will be given medicine to make you relaxed or sleep. In a trauma patient, the clinical triad of altered mental status, unilateral pupillary dilatation with loss of light reflex, and contralateral hemiparesis is most often due to upper brainstem compression by uncal transtentorial herniation which, in the majority of trauma cases, is due to an extraaxial intracranial hematoma. He walked out of the hospital a month later. To prevent the head from shifting under this pressure have an assistant brace the head. Kudos to you sir for keeping your cool and thanks for sharing your experiences. 3. This clot will be gelatinous in consistency and drainage through a single burr hole can be difficult. The Neurosurgeon will later trim and repair the bony defect. They will inject numbing medicine into your scalp. 1) We find it easier, when encountered a clot that wont extrude, to irrigate gently with sterile saline. D. CT scan of a subdural hematoma. The use of anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents by the patient increases their risk of hemorrhagic complications. But a head injury results in the tear of these blood vessels and bleeding occurs. He initially appeared well and was running around the triage room. Anatomical landmarks suggestive for placement of the catheter within the ventricular system are to insert the catheter perpendicular to the skull and directed toward the ipsilateral inner canthus.2 Advance the catheter to a depth of approximately 5 to 6 cm. burr hole subdural outcome hematoma chronic aesthetic trepanation improve covers placement improving retrospective evacuation pilot study Your surgeon will use a special drill to insert the burr hole into the skull. burr hole cranial emergency procedures decompression cranium crackin common ed emdocs location considerations tricks unlocking tips In the severely head-injured patient, a multitude of coagulopathic abnormalities can occur including hypercoagulable and fibrinolytic states as well as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Mjovsk, M., Netuka, D., Bene, V. & Kucera, P. Burr-hole evacuation of chronic subdural hematoma: Biophysically and evidence-based technique improvement. The perforator bits have a sharp point. They are used to enlarge the hole in the skull made by the perforator bit (Figure 116-6). In order to access the brain tissue, surgeons will open the skull to get access to the brain. Shave the hair with clippers; sterile prep and drape. This site uses cookies to provide, maintain and improve your experience. The patient was running around the emergency department with no deficits and gave me a hug. A significant proportion of patients with fatal head injuries die before reaching the hospital. There are three common methods for performing trephinations:2, Figure 3. Drilling a series of small holes and connecting them, Making crosshatch cuts in the bone and connecting them to remove a rectangular piece of bone. Close the scalp/skin with 3-0 nylon suture. The skull shows four separate holes made by trephination that had begun to heal, indicating that the patient survived the procedure. Probe the disc of bone and if loose, pick it up with Kelly forceps. If the blood continues to build, it may cause coma and brain damage. Conservative vs. Surgical Management of Post-Traumatic Epidural Hematoma: A Case A prospective study found that the most common organism responsible for post-operative central nervous system infections was. J.E. Ghajar JBG: A guide for ventricular catheter placement: technical note. A key indication is that there should be no accessible neurosurgeon available to perform the procedure. Frequently remove the burr bit to examine the hole. Galt trephine. Your surgeon will shave and remove the hair of the area and give a small incision in the scalp to expose your skull. The assessment should include hemodynamic parameters, Glasgow Coma Score, and frequent neurological examinations. 2010 Sep;39(3):377-83. Postprocedural treatment often requires airway protection with continued endotracheal intubation, adequate fluid resuscitation, management of hypoxia, management of hypotension, management of seizures, and management of any coagulopathy. A. Create an environment that will facilitate ease of procedure, including positioning patient and ensuring easy access to equipment. ICH is rare in the posterior fossa, comprising only 4 to 13% of acute EDH and 1% of acute SDH. Provides access to middle fossa (the most common site of epidural hematoma) and usually allows access to most convexity subdural hematomas, as well as proximity to middle meningeal artery in region of pterion, 2.if no epidural hematoma, the dura is opened if it has bluish discoloration (suggests subdural hematoma(SDH)) or if there is a strong suspicion of a mass lesion on that side, 3. if completely negative, usually perform temporal burr hole on contralateral side, 4. if negative, further burr holes should be undertaken if a CT cannot now be done, 5. proceed to ipsilateral frontal burr hole. NLM/Science Source. Surgeons will use this hole to drain blood or other fluid causing pressure on the brain. We have learned a few practical things at our institution that I would like to share: A regular course of antibiotics will prevent any post-surgical infections in the surgical site. Aggressive management of hypoxia and hypotension cannot be overemphasized. J Neurotrauma. The dura is exposed and a hematoma is visible below it. Emergency Twist Drill Trephination. failure to improve with mannitol and hyperventilation), and CT scan cannot be performed and interpreted immediately, then treatment should not wait for CT scan, a) in general, if the O.R. Grasp the rotating handle with the dominant hand. Rapid evacuation of an intracranial hematoma may help to improve the outcome. Exercising extreme caution during the maneuver is mandatory to prevent lacerating the brain. 10.1089/089771502320317140.
Gently separate the dura from the skull. I performed the burr hole with the technique described below and evacuated 150 mL of blood. Other complications include plunging with the perforator bit or the burr bit resulting in a penetrating injury to the brain, cortical lacerations, cortical contusions, and seizures. Take small bites of the skull to enlarge the hole (Figure 116-8E). Position the patient so that the proposed incision site is visible and easily accessible. Ideally, these patients are resuscitated and a CT scan of the head is completed in order to determine the presence of an intracranial hematoma. Use suction to remove the bone fragments and the irrigation fluid. Once this incision is made, use the mosquito forceps to move the periosteum to the side and allow the self-retaining retractor to be placed along the periosteum. The bone fragment may come out in the device or may need to be removed with forceps.
were positive in 56%.
Orotracheally intubate the patient to protect and secure the airway. What if there is no neurosurgery service at your hospital? An incision is made through the skin, subcutaneous tissue, temporalis muscle, and galea aponeurotica.
Talk with your healthcare provider to find out what risks may apply to you. Remove the periosteum overlying the skull by scraping it away with a periosteal elevator. Six patients had significant extraaxial hematomas missed with exploratory burr holes (mostly due to incomplete burr hole exploration). Temporal 2 finger-breadths above and 2 finger-breadths forward of the auditory canal, Frontal 10 cm above eye in mid-pupillary line (about 3 cm from sagittal suture), *Posterior fossa- 3 cm medial to the easily palpated mastoid eminence, A posterior cranial fossa burr hole may be considered. At no time should any pressure be placed on the brain. Using an IO device to make a circle of small holes and connect them has been described. Burr holes are primarily a diagnostic tool, as bleeding cannot be controlled and most acute hema- tomas are too congealed to be removed through a burr hole. The periosteum will otherwise get caught in the perforator bit and make it difficult to turn. Free the underlying dura from the bone edge with a Penfield elevator. subdural subgaleal neurosurgery Intubation utilizing the rapid sequence technique often precedes burr hole placement in the patient with severe head injury. burr subdural subperiosteal sdd drainage hematoma performed The pupils improved. Continue to drill until the inner table has been penetrated or the perforator bit locks (Figure 116-8C). 1. PubMed PMID: In contrast, a small tear cause blood to build up more slowly. Other sources of epidural hematomas include a torn venous sinus or an injury to the carotid artery before it enters the intracranial dural mater. After the neurosurgeon determines the suitable location, the process starts. Hematomas are usually found ipsilateral to the pupillary change in up to 85% of cases. However, having cautery available can be helpful. Burr hole evacuation in a trauma setting should be considered only in the presence of rapid neurological deterioration with evidence of herniation and brainstem compression and the unavailability of a Neurosurgeon to perform the procedure. Do not concern yourself with making the hole smooth or symmetric. Would technique differ in any way? Lower rates in younger patients (<30 yrs) and those in MVAs (as opposed to falls or assaults). Patients who have had burr hole placement because of neurological deterioration require further definitive management by a Neurosurgeon. Check out our new downloadable procedure card with QR code link to the article. Indications in E/R (rare): patient dying of rapid transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression that does not improve or stabilize with mannitol and hyperventilation Thanks. If unsuccessful after three attempts, place the parenchymal monitor or a subarachnoid bolt. Epidural and subdural hemorrhages are usually clotted in the acute stages. Apply traction on the suture to elevate the dura. D. The hole is enlarged with a burr bit on the Hudson brace drill. This procedure may be performed by trained Emergency Physicians if a Neurosurgeon has been consulted and is not immediately available. This should include sterile gloves, a sterile gown, a face mask with an eye shield or goggles, and a cap. The patient becomes more somnolent and bradycardic. Sinai St. Lukes West) // Reviewed by: Anthony DeVivo, DO (Critical Care Fellow, Icahn School of Medicine-Mount Sinai Hospital); Alex Koyfman, MD (@EMHighAK); Brit Long, MD (@long_brit); Manpreet Singh, MD (@MPrizzleER). We placed a sterile dressing on the wound, and the helicopter team transported the patient to the pediatric trauma center. Obtain an informed consent. Grasp the stabilizing handle of the Hudson brace with the nondominant hand. craniotomy vs craniectomy keyhole supratentorial chronic trepanation burr subdural hematoma hole decompressive ich considerations anesthetic tumors awake ppt powerpoint presentation Administer a broad-spectrum antibiotic that covers gram-positive skin flora. The contents of the hospital-prepared burr hole tray. Print them out and be ready to go over it with your learners! After intubation the patient should be appropriately sedated with amnestic and analgesic medications. An immediate, sudden rupture might cause blood to build up very quickly.
It is possible to run sterile saline onto the skull to both remove debris and to keep the friction heat to a minimum. Obtain a complete blood count (hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count) and a coagulation profile (PT, PTT, and INR) to ensure that the patient is not thrombocytopenic or coagulopathic. Or he or she may close the dura and scalp right away. 1960; 2:167172, Andrews BT, Pitts LH, Lovely MP, et al. The patient should be fully monitored with a noninvasive blood pressure cuff, pulse oximetry, cardiac monitor, and end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor (if available). Lancet. 6. subsequent burr holes may be placed at parietal region and lastly in posterior fossa. The temporal burr hole is made two finger breadths above the zygomatic arch and two finger breadths anterior to the external auditory meatus (Figure 116-7B).
B. Lateral view of the skull. A 2-year-old male was brought to the emergency department by his mother after falling out of a shopping cart seat and striking his head. The guard should be set at the appropriate depth. Emergency department skull trephinations should only be performed in the temporal region to avoid venous sinus injury and complications of air embolism or hemorrhage. Turn the rotating handle clockwise with the dominant hand using a smooth and slow motion. https://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=683§ionid=45343759.
A coagulopathy or thrombocytopenia makes a burr hole dangerous to perform. Exercise extreme caution as the bit does not always lock when the inner table is perforated. Thesurgery teamwill trim the hair on your scalp in the area of surgery. However, exercise extreme caution as the bit may occasionally not lock when it penetrates the inner table of the skull.
Authors: Edmund Hsu, MD (EM Resident Physician, Mt. burr emergency holes figure The burr bits are rounded.
I intubated him and called the nearest pediatric trauma center (one hour away) to begin arranging for helicopter transport. The two nonautomated choices for trephine are the Integra hand crank model with stopper (see Figure 1) and the Galt trephine (see Figure 2). Irrigate the area. Allow the povidone iodine or chlorhexidine solution to dry. Place the tip of the perforator bit against the skull (Figure 116-8B). Outcome may possibly be improved slightly by increasing the rapidity with which decompression is undertaken, however, an upper limit of salvageability is probably still only 20% satisfactory outcome. Furthermore, the prognosis of patients with traumatic herniation is poor. When expanded, this should create a clear path directly down to the bone. 4). Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may not immediately extrude. Watch as the perforator bit cuts through the skull. Terms of Use If the blood has clotted run some sterile saline over the area to softly break it up. Measure the skull thickness on CT to set stopper depth on the Integra skull trephination kit with adjustable stopper. Gently probe the hole to determine if the inner table has been penetrated. is foreseen, emergency burr holes in the E/R should be performed, 2. placement of burrhole(s) as outlined under Technique. The Hudson brace drill is a handheld device (Figure 116-4). This will allow easier access to the area of the skull that you are trying to access. The placement of a temporal burr hole on the side of the mydriatic pupil to decompress an epidural or subdural hematoma can be lifesaving. subdural hematoma preoperative Sinai St. Lukes West) and Nicholas Buffin, MD (EM Resident Physician, Mt. 2022. Make a nick in the dural with an 18 gauge needle or a #11 scalpel blade. The perforator bit is used to make a hole through the skull and just penetrate the inner table of bone. A. burr hole shot am cranium procedures cranial crackin decompression common ed emdocs screen unlocking Postprocedural CT scanning should not be performed if definitive management by a Neurosurgeon is available. Avoid lacerating the middle meningeal artery or its branches. A Hudson brace drill fitted with a perforator bit is used to penetrate the skull to the inner table. dbs leads stimulation brain deep scientific boston accessories lead burr hole bostonscientific kit Burr holes can be lifesaving on rare occasions when the patient is worsening neurologically or has blown a pupil and CT scan is unavailable.
 This is when blood slowly builds up under the dura layerafter a mild head injury. Temporising an extradural haematoma by intraosseous needle craniostomy in the District General Hospital by non-neurosurgical doctors A case report. Turn the head to the contralateral side if the cervical spine has been cleared. Smith SW, Clark M, Nelson J, et al.
This is when blood slowly builds up under the dura layerafter a mild head injury. Temporising an extradural haematoma by intraosseous needle craniostomy in the District General Hospital by non-neurosurgical doctors A case report. Turn the head to the contralateral side if the cervical spine has been cleared. Smith SW, Clark M, Nelson J, et al.  The bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes (Figure 116-5). Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy. Enter your email address to receive notifications of new posts by email. a) indicators of transtentorial herniation/brainstem compression: sudden drop in Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, paralysis or decerebration develops (usually contralateral to blown pupil). Always maintain the drill perpendicular to the skull. seong soonchunhyang maximal burr indications versus Your email address will not be published. I had seen one of these in residency and went to the supply room to find the newly arrived burr hole kit, took a deep breath, then started to prepare for the procedure by reviewing the CT.
The bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes (Figure 116-5). Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy. Enter your email address to receive notifications of new posts by email. a) indicators of transtentorial herniation/brainstem compression: sudden drop in Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, paralysis or decerebration develops (usually contralateral to blown pupil). Always maintain the drill perpendicular to the skull. seong soonchunhyang maximal burr indications versus Your email address will not be published. I had seen one of these in residency and went to the supply room to find the newly arrived burr hole kit, took a deep breath, then started to prepare for the procedure by reviewing the CT. The veins there are fragile and easy to break, especially in older adults. However, if the burr hole is positive, it is possible that modest decompression may be performed, and then the definitive craniotomy can be undertaken incorporating the burr hole(s). articular beneath bereiter indications (equipped to handle craniotomy, better lighting and sterility, dedicated scrub nurse) especially in older patients (>30 yrs) not involved in MVAs. Other contraindications include localized infections of the scalp and patients who are thrombocytopenic. CT scanning also verifies catheter location and reduction in ventricular size in patients in which trephination has been completed for ventricular catheter placement. https://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=683§ionid=45343759. The below instructions are for a temporal ICH (intracranial hematoma epidural/subdural), which is the most common ICH. The clot of an epidural hematoma will be obvious as it separates the inner table of the skull from the dura. This makes it more vulnerable to a fracture with an associated injury to the underlying middle meningeal vessels. The general steps include 4: After this operation, youll move to the recovery place and stay in the hospital for 1 or 2 days. The prognosis for the severely head-injured patient with clinical evidence of tentorial herniation and brainstem compression is poor. Perform a time out to ensure that everyone involved is aware of the patient identity, the plan for the coming procedure, why the procedure is being performed, and the side on which the procedure will occur.
Examples of perforator bits (left) and burr bits (right). 2007, 21 (1): 11-15. Turn the crank slowly and smoothly, while continuing to apply pressure. A 53-year-old female with no significant past medical history presents to the Emergency Department (ED) with headache after syncope while on a treadmill. The distal end has a snap lock chuck that slides to allow easy insertion and removal of the bits. Confirm skull thickness on CT as seen below in figure 1. You elevate the head of the bed and start IV antihypertensives. Fit the Hudson brace drill with a perforator bit. Notify me of follow-up comments by email. SDH was the most common extraaxial mass lesion (alone and unilateral in 70%, bilateral in 1 1 %, and in combination with EDH or ICH in > 9 %) . Check often for the bone fragment in the instrument. Another option is to obtain a lateral plain radiograph of the skull. Prophylactic intravenous antibiotic coverage is recommended if time permits. The frontal burr hole can be used to drain an intracranial hematoma or to perform a ventriculostomy. trauma, 4. if no localizing clues, place hole on left side (to evaluate and decompress the dominant Cranioplasty is often not completed initially after burr hole placement in order to minimize the infectious risk. exploratory burr holes (bilateral temporal, frontal and parietal, done in the O.R.) Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Use a small sterile pediatric suction catheter to facilitate hematoma drainage. A head CT revealed a large epidural hematoma with midline shift.
 Its sounds just like one of those scenes from those medical dramas. After intubation what are your next steps? An error has occurred sending your email(s). B. CT scan of an epidural hematoma. Infiltrate 5 mL of lidocaine containing epinephrine along the proposed incision site and down to the level of the periosteum on the skull. A large area of the temporal region is shaved and prepared in a sterile manner with betadine/chlorhexidine and a local anesthetic injected subcutaneously using a 25G needle. Like other surgical operations, burr hole surgery comprises some risks during and after operation. Hemostasis can often be obtained with the use of the retractor. This includes pupillary dilation with a decreased or absent light reflex, progressive deterioration in the patient's level of consciousness, and/or hemiparesis including posturing (decerebrate/decorticate) or flaccidity. Wilson, M.H., Wise, D., Davies, G. et al. Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may extrude spontaneously or require gentle suction with a catheter. Have an assistant hold the patients head firmly prior to drilling. The risk of surgical complications is even higher in this area; therefore, it should be pursued only as a last resort or if there is obvious injury only to this area.8, Your email address will not be published. bifrontal craniotomy supraorbital The surgeon will make a cut (incision) in your scalp. Rotate the handle clockwise to enlarge the hole in the skull (Figure 116-8D). During the conversation with the trauma surgeon at the major academic center, I told him I was planning on doing an emergent burr hole. However, when they do occur, they signify cerebral compression and transtentorial herniation. This builds up of blood eventually can lead to death while left untreated. I ordered the necessary kits so we would have the tools on-site. Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license:CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International. Controversial. Remove the perforator bit from the Hudson brace drill. Durnford S, Bulstrode H, Durnford A, Chakraborty A, Tarmey NT. Extradural Hematoma: Observations on 125 Cases. Finally, your surgeon will close this hole or left it open with a drain or shunt attached. Wellcome Images/Science Source, Topics: Burr HoleCase ReportsCritical CareEmergency DepartmentEmergency MedicineEmergency Physicianshead injuryPatient CareTrauma and InjuryTrephination. Hold the Hudson brace drill as described above. Prophylactic antibiotics covering gram positive organisms should be considered at this time. 120-122. Accessibility
undergoing transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression as outlined above, Emergency department skull trephinations are done in the temporal location 2 cm anterior and 2 cm superior to the tragus.1, Trephinations of the skull have been found in human skulls older than 10,000 years of age. My partner drilled on an elderly man comatose with herniating SDH. Suspect a space-occupying lesion when there is clinical evidence of tentorial herniation or upper brain stem dysfunction.
Its sounds just like one of those scenes from those medical dramas. After intubation what are your next steps? An error has occurred sending your email(s). B. CT scan of an epidural hematoma. Infiltrate 5 mL of lidocaine containing epinephrine along the proposed incision site and down to the level of the periosteum on the skull. A large area of the temporal region is shaved and prepared in a sterile manner with betadine/chlorhexidine and a local anesthetic injected subcutaneously using a 25G needle. Like other surgical operations, burr hole surgery comprises some risks during and after operation. Hemostasis can often be obtained with the use of the retractor. This includes pupillary dilation with a decreased or absent light reflex, progressive deterioration in the patient's level of consciousness, and/or hemiparesis including posturing (decerebrate/decorticate) or flaccidity. Wilson, M.H., Wise, D., Davies, G. et al. Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may extrude spontaneously or require gentle suction with a catheter. Have an assistant hold the patients head firmly prior to drilling. The risk of surgical complications is even higher in this area; therefore, it should be pursued only as a last resort or if there is obvious injury only to this area.8, Your email address will not be published. bifrontal craniotomy supraorbital The surgeon will make a cut (incision) in your scalp. Rotate the handle clockwise to enlarge the hole in the skull (Figure 116-8D). During the conversation with the trauma surgeon at the major academic center, I told him I was planning on doing an emergent burr hole. However, when they do occur, they signify cerebral compression and transtentorial herniation. This builds up of blood eventually can lead to death while left untreated. I ordered the necessary kits so we would have the tools on-site. Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license:CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International. Controversial. Remove the perforator bit from the Hudson brace drill. Durnford S, Bulstrode H, Durnford A, Chakraborty A, Tarmey NT. Extradural Hematoma: Observations on 125 Cases. Finally, your surgeon will close this hole or left it open with a drain or shunt attached. Wellcome Images/Science Source, Topics: Burr HoleCase ReportsCritical CareEmergency DepartmentEmergency MedicineEmergency Physicianshead injuryPatient CareTrauma and InjuryTrephination. Hold the Hudson brace drill as described above. Prophylactic antibiotics covering gram positive organisms should be considered at this time. 120-122. Accessibility
undergoing transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression as outlined above, Emergency department skull trephinations are done in the temporal location 2 cm anterior and 2 cm superior to the tragus.1, Trephinations of the skull have been found in human skulls older than 10,000 years of age. My partner drilled on an elderly man comatose with herniating SDH. Suspect a space-occupying lesion when there is clinical evidence of tentorial herniation or upper brain stem dysfunction. Position patient in supination and elevate the shoulder ipsilateral to the ICH with a shoulder roll. Place the burr bit into the hole in the skull. The coronal suture is often palpable. When burr holes were positive, the first burr hole was on the correct side 86% of the time when placed as suggested above. Mahoney BD, Rockswold GL, Ruiz E, Clinton JE. Irrigate the area. Contact us at [emailprotected]. You will be given medicine to make you relaxed or sleep. In a trauma patient, the clinical triad of altered mental status, unilateral pupillary dilatation with loss of light reflex, and contralateral hemiparesis is most often due to upper brainstem compression by uncal transtentorial herniation which, in the majority of trauma cases, is due to an extraaxial intracranial hematoma. He walked out of the hospital a month later. To prevent the head from shifting under this pressure have an assistant brace the head. Kudos to you sir for keeping your cool and thanks for sharing your experiences. 3. This clot will be gelatinous in consistency and drainage through a single burr hole can be difficult. The Neurosurgeon will later trim and repair the bony defect. They will inject numbing medicine into your scalp. 1) We find it easier, when encountered a clot that wont extrude, to irrigate gently with sterile saline. D. CT scan of a subdural hematoma. The use of anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents by the patient increases their risk of hemorrhagic complications. But a head injury results in the tear of these blood vessels and bleeding occurs. He initially appeared well and was running around the triage room. Anatomical landmarks suggestive for placement of the catheter within the ventricular system are to insert the catheter perpendicular to the skull and directed toward the ipsilateral inner canthus.2 Advance the catheter to a depth of approximately 5 to 6 cm. burr hole subdural outcome hematoma chronic aesthetic trepanation improve covers placement improving retrospective evacuation pilot study Your surgeon will use a special drill to insert the burr hole into the skull. burr hole cranial emergency procedures decompression cranium crackin common ed emdocs location considerations tricks unlocking tips In the severely head-injured patient, a multitude of coagulopathic abnormalities can occur including hypercoagulable and fibrinolytic states as well as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Mjovsk, M., Netuka, D., Bene, V. & Kucera, P. Burr-hole evacuation of chronic subdural hematoma: Biophysically and evidence-based technique improvement. The perforator bits have a sharp point. They are used to enlarge the hole in the skull made by the perforator bit (Figure 116-6). In order to access the brain tissue, surgeons will open the skull to get access to the brain. Shave the hair with clippers; sterile prep and drape. This site uses cookies to provide, maintain and improve your experience. The patient was running around the emergency department with no deficits and gave me a hug. A significant proportion of patients with fatal head injuries die before reaching the hospital. There are three common methods for performing trephinations:2, Figure 3. Drilling a series of small holes and connecting them, Making crosshatch cuts in the bone and connecting them to remove a rectangular piece of bone. Close the scalp/skin with 3-0 nylon suture. The skull shows four separate holes made by trephination that had begun to heal, indicating that the patient survived the procedure. Probe the disc of bone and if loose, pick it up with Kelly forceps. If the blood continues to build, it may cause coma and brain damage. Conservative vs. Surgical Management of Post-Traumatic Epidural Hematoma: A Case A prospective study found that the most common organism responsible for post-operative central nervous system infections was. J.E. Ghajar JBG: A guide for ventricular catheter placement: technical note. A key indication is that there should be no accessible neurosurgeon available to perform the procedure. Frequently remove the burr bit to examine the hole. Galt trephine. Your surgeon will shave and remove the hair of the area and give a small incision in the scalp to expose your skull. The assessment should include hemodynamic parameters, Glasgow Coma Score, and frequent neurological examinations. 2010 Sep;39(3):377-83. Postprocedural treatment often requires airway protection with continued endotracheal intubation, adequate fluid resuscitation, management of hypoxia, management of hypotension, management of seizures, and management of any coagulopathy. A. Create an environment that will facilitate ease of procedure, including positioning patient and ensuring easy access to equipment. ICH is rare in the posterior fossa, comprising only 4 to 13% of acute EDH and 1% of acute SDH. Provides access to middle fossa (the most common site of epidural hematoma) and usually allows access to most convexity subdural hematomas, as well as proximity to middle meningeal artery in region of pterion, 2.if no epidural hematoma, the dura is opened if it has bluish discoloration (suggests subdural hematoma(SDH)) or if there is a strong suspicion of a mass lesion on that side, 3. if completely negative, usually perform temporal burr hole on contralateral side, 4. if negative, further burr holes should be undertaken if a CT cannot now be done, 5. proceed to ipsilateral frontal burr hole. NLM/Science Source. Surgeons will use this hole to drain blood or other fluid causing pressure on the brain. We have learned a few practical things at our institution that I would like to share: A regular course of antibiotics will prevent any post-surgical infections in the surgical site. Aggressive management of hypoxia and hypotension cannot be overemphasized. J Neurotrauma. The dura is exposed and a hematoma is visible below it. Emergency Twist Drill Trephination. failure to improve with mannitol and hyperventilation), and CT scan cannot be performed and interpreted immediately, then treatment should not wait for CT scan, a) in general, if the O.R. Grasp the rotating handle with the dominant hand. Rapid evacuation of an intracranial hematoma may help to improve the outcome. Exercising extreme caution during the maneuver is mandatory to prevent lacerating the brain. 10.1089/089771502320317140.
Gently separate the dura from the skull. I performed the burr hole with the technique described below and evacuated 150 mL of blood. Other complications include plunging with the perforator bit or the burr bit resulting in a penetrating injury to the brain, cortical lacerations, cortical contusions, and seizures. Take small bites of the skull to enlarge the hole (Figure 116-8E). Position the patient so that the proposed incision site is visible and easily accessible. Ideally, these patients are resuscitated and a CT scan of the head is completed in order to determine the presence of an intracranial hematoma. Use suction to remove the bone fragments and the irrigation fluid. Once this incision is made, use the mosquito forceps to move the periosteum to the side and allow the self-retaining retractor to be placed along the periosteum. The bone fragment may come out in the device or may need to be removed with forceps.
were positive in 56%.
Orotracheally intubate the patient to protect and secure the airway. What if there is no neurosurgery service at your hospital? An incision is made through the skin, subcutaneous tissue, temporalis muscle, and galea aponeurotica.
Talk with your healthcare provider to find out what risks may apply to you. Remove the periosteum overlying the skull by scraping it away with a periosteal elevator. Six patients had significant extraaxial hematomas missed with exploratory burr holes (mostly due to incomplete burr hole exploration). Temporal 2 finger-breadths above and 2 finger-breadths forward of the auditory canal, Frontal 10 cm above eye in mid-pupillary line (about 3 cm from sagittal suture), *Posterior fossa- 3 cm medial to the easily palpated mastoid eminence, A posterior cranial fossa burr hole may be considered. At no time should any pressure be placed on the brain. Using an IO device to make a circle of small holes and connect them has been described. Burr holes are primarily a diagnostic tool, as bleeding cannot be controlled and most acute hema- tomas are too congealed to be removed through a burr hole. The periosteum will otherwise get caught in the perforator bit and make it difficult to turn. Free the underlying dura from the bone edge with a Penfield elevator. subdural subgaleal neurosurgery Intubation utilizing the rapid sequence technique often precedes burr hole placement in the patient with severe head injury. burr subdural subperiosteal sdd drainage hematoma performed The pupils improved. Continue to drill until the inner table has been penetrated or the perforator bit locks (Figure 116-8C). 1. PubMed PMID: In contrast, a small tear cause blood to build up more slowly. Other sources of epidural hematomas include a torn venous sinus or an injury to the carotid artery before it enters the intracranial dural mater. After the neurosurgeon determines the suitable location, the process starts. Hematomas are usually found ipsilateral to the pupillary change in up to 85% of cases. However, having cautery available can be helpful. Burr hole evacuation in a trauma setting should be considered only in the presence of rapid neurological deterioration with evidence of herniation and brainstem compression and the unavailability of a Neurosurgeon to perform the procedure. Do not concern yourself with making the hole smooth or symmetric. Would technique differ in any way? Lower rates in younger patients (<30 yrs) and those in MVAs (as opposed to falls or assaults). Patients who have had burr hole placement because of neurological deterioration require further definitive management by a Neurosurgeon. Check out our new downloadable procedure card with QR code link to the article. Indications in E/R (rare): patient dying of rapid transtentorial herniation or brainstem compression that does not improve or stabilize with mannitol and hyperventilation Thanks. If unsuccessful after three attempts, place the parenchymal monitor or a subarachnoid bolt. Epidural and subdural hemorrhages are usually clotted in the acute stages. Apply traction on the suture to elevate the dura. D. The hole is enlarged with a burr bit on the Hudson brace drill. This procedure may be performed by trained Emergency Physicians if a Neurosurgeon has been consulted and is not immediately available. This should include sterile gloves, a sterile gown, a face mask with an eye shield or goggles, and a cap. The patient becomes more somnolent and bradycardic. Sinai St. Lukes West) // Reviewed by: Anthony DeVivo, DO (Critical Care Fellow, Icahn School of Medicine-Mount Sinai Hospital); Alex Koyfman, MD (@EMHighAK); Brit Long, MD (@long_brit); Manpreet Singh, MD (@MPrizzleER). We placed a sterile dressing on the wound, and the helicopter team transported the patient to the pediatric trauma center. Obtain an informed consent. Grasp the stabilizing handle of the Hudson brace with the nondominant hand. craniotomy vs craniectomy keyhole supratentorial chronic trepanation burr subdural hematoma hole decompressive ich considerations anesthetic tumors awake ppt powerpoint presentation Administer a broad-spectrum antibiotic that covers gram-positive skin flora. The contents of the hospital-prepared burr hole tray. Print them out and be ready to go over it with your learners! After intubation the patient should be appropriately sedated with amnestic and analgesic medications. An immediate, sudden rupture might cause blood to build up very quickly.
It is possible to run sterile saline onto the skull to both remove debris and to keep the friction heat to a minimum. Obtain a complete blood count (hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count) and a coagulation profile (PT, PTT, and INR) to ensure that the patient is not thrombocytopenic or coagulopathic. Or he or she may close the dura and scalp right away. 1960; 2:167172, Andrews BT, Pitts LH, Lovely MP, et al. The patient should be fully monitored with a noninvasive blood pressure cuff, pulse oximetry, cardiac monitor, and end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor (if available). Lancet. 6. subsequent burr holes may be placed at parietal region and lastly in posterior fossa. The temporal burr hole is made two finger breadths above the zygomatic arch and two finger breadths anterior to the external auditory meatus (Figure 116-7B).
B. Lateral view of the skull. A 2-year-old male was brought to the emergency department by his mother after falling out of a shopping cart seat and striking his head. The guard should be set at the appropriate depth. Emergency department skull trephinations should only be performed in the temporal region to avoid venous sinus injury and complications of air embolism or hemorrhage. Turn the rotating handle clockwise with the dominant hand using a smooth and slow motion. https://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=683§ionid=45343759.
A coagulopathy or thrombocytopenia makes a burr hole dangerous to perform. Exercise extreme caution as the bit does not always lock when the inner table is perforated. Thesurgery teamwill trim the hair on your scalp in the area of surgery. However, exercise extreme caution as the bit may occasionally not lock when it penetrates the inner table of the skull.
Authors: Edmund Hsu, MD (EM Resident Physician, Mt. burr emergency holes figure The burr bits are rounded.
I intubated him and called the nearest pediatric trauma center (one hour away) to begin arranging for helicopter transport. The two nonautomated choices for trephine are the Integra hand crank model with stopper (see Figure 1) and the Galt trephine (see Figure 2). Irrigate the area. Allow the povidone iodine or chlorhexidine solution to dry. Place the tip of the perforator bit against the skull (Figure 116-8B). Outcome may possibly be improved slightly by increasing the rapidity with which decompression is undertaken, however, an upper limit of salvageability is probably still only 20% satisfactory outcome. Furthermore, the prognosis of patients with traumatic herniation is poor. When expanded, this should create a clear path directly down to the bone. 4). Once the bone fragment is removed, the clot may not immediately extrude. Watch as the perforator bit cuts through the skull. Terms of Use If the blood has clotted run some sterile saline over the area to softly break it up. Measure the skull thickness on CT to set stopper depth on the Integra skull trephination kit with adjustable stopper. Gently probe the hole to determine if the inner table has been penetrated. is foreseen, emergency burr holes in the E/R should be performed, 2. placement of burrhole(s) as outlined under Technique. The Hudson brace drill is a handheld device (Figure 116-4). This will allow easier access to the area of the skull that you are trying to access. The placement of a temporal burr hole on the side of the mydriatic pupil to decompress an epidural or subdural hematoma can be lifesaving. subdural hematoma preoperative Sinai St. Lukes West) and Nicholas Buffin, MD (EM Resident Physician, Mt. 2022. Make a nick in the dural with an 18 gauge needle or a #11 scalpel blade. The perforator bit is used to make a hole through the skull and just penetrate the inner table of bone. A. burr hole shot am cranium procedures cranial crackin decompression common ed emdocs screen unlocking Postprocedural CT scanning should not be performed if definitive management by a Neurosurgeon is available. Avoid lacerating the middle meningeal artery or its branches. A Hudson brace drill fitted with a perforator bit is used to penetrate the skull to the inner table. dbs leads stimulation brain deep scientific boston accessories lead burr hole bostonscientific kit Burr holes can be lifesaving on rare occasions when the patient is worsening neurologically or has blown a pupil and CT scan is unavailable.