Whichever mode one chooses, one needs to be aware of the limitations of that mode. "@type": "ImageObject", Nasal pillows. ", "description": "Pressure cycled are often triggered by flow sensing reducing work of breathing. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/20/Full+Ventilation+Noninvasive+or+invasive.jpg", { "description": "Fewer hospitalizations. Allows facial freedom. Outcomes. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/8/Patients+Cardiopulmonary+stability.jpg",
Complications. "@context": "http://schema.org", Whichever mode one chooses, one needs to be aware of the limitations of that mode. Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilationAfter and acute illness After prolonged ventilation for a chronic disease Progressive chronic respiratory failure Sleep disturbance Central or obstructive, apnea or hypopnea "description": "Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath", "@type": "ImageObject", "description": "Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography. { EPAP\u2014the expiratory positive airway pressure--CPAP. Tracheostomies
The ventilator generates pressure support by adding flow to the circuit during patient-triggered breaths in IMV or SIMV modes. obstructive airway "contentUrl": "https://images.slideplayer.com/19/5879828/slides/slide_32.jpg", { "name": "", To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that "@type": "ImageObject", "width": "800" "@type": "ImageObject", "@context": "http://schema.org", BiPAP Pressure Support VentilationIPAPthe inspiratory positive airway pressureextra help when breathing in EPAPthe expiratory positive airway pressure--CPAP Cycles based on patient initiated breaths Available with timed back-up rates Used for severe sleep apnea, neuromuscular weakness or insufficiency SIMV modes are used to wean patients; as you decrease the set rate, the patient will need to do more on their own to maintain normal blood gases. "@context": "http://schema.org", "name": "Indications\/Criteria", Nursing support arranged for nighttime. Risk of hyperventilation if agitated. Bilevel Mode Mimic BiPAP / No Backup Rate an opening must be attempted in the trunk of the trachea, into which a tube of reed or cane should be put; you will then blow into this, so that the. Increased work of breathing vs. "width": "800" Especially on exertion or lying down. Restlessness and anxiety. Flow-cycled.
Stamina for play or daily activities while ventilated. "description": "Pressure cycled or volume cycled. "@context": "http://schema.org", This is usually because the patients lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. Home considerations. "name": "CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure For simple sleep apnea",
Outline Indications Patients Interfaces VentilatorsModes of ventilation Home considerations Complications Outcomes { "@type": "ImageObject", "description": "Forced vital capacity < 50% predicted. { Community support. { "width": "800" Bronchoscopy. "description": "Reduce morbidity. "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" tidal volume by change suddenly as patients compliance changes, this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung, if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease, no limit per se on PIP (usually vent will have upper pressure limit), square wave(constant) flow pattern results in higher PIP for same tidal volume as compared to Pressure modes. "width": "800" SIMV Mode Most patients, improved comfort, stable CO2s "name": "Noninvasive interfaces", ", Increasing peak pressures on volume mode (or decreasing tidal volumes in pressure modes) can also be a sign that the ETT is obstructed or of another problem with the ventilator circuit.
Note that for the paralyzed patient there is no significant difference between assist control and SIMV. Potential hypoventilation or overexpansion. { "width": "800" Cycles based on patient initiated breaths.
Regardless of the parameter that is controlled, the other must be monitored as it is a reflection of the compliance and hence the patients pulmonary function. "width": "800" }, 9 { Nesreen El-Sayed Morsy Aly Thoracic Medicine Department, D. Sara Salarian,. "@context": "http://schema.org", { "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Pressure Limited", Control vs. SIMV CONTROL MODE SIMV MODE Every breath fully supportedCant wean by decreasing rate Risk of hyperventilation if agitated SIMV MODE Vent synchronizes to support patient effort Patient takes own breaths between vent breaths Increased work of breathing vs. control { { "description": "Every breath is supported regardless of trigger Can\u2019t wean by decreasing rate. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. "@context": "http://schema.org", "name": "Bilevel Mode Mimic BiPAP \/ No Backup Rate",
Patients placed on control modes are often deeply sedated and may be given neuromuscular blockers. Better control of ventilation than oxygenation. ", "description": "Cori Daines, MD. "width": "800" "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/40/Continuing+Assessment.jpg", Better sleep quality. Home Mechanical VentilationCori Daines, MD Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine ATS Position Paper", Can be given with spontaneous breaths in IMV modes or as stand alone mode without set rate. "description": "Setting capabilities. VOLUME-LIMITED Accept that changes in compliance may lead to increases in peak airway pressures and associated baro/volutrauma. "name": "NIV: Nasal mask \/ Prongs", "@type": "ImageObject", ", ", Full Ventilation Noninvasive or invasivePressure cycled or volume cycled SIMV vs. AC Allows pressure support, PEEP, inspiratory time, flow to be added and manipulated "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/41/Complications+Ventilator+failure+Tracheostomy+issues.jpg", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. "name": "Home ventilation reality", "@type": "ImageObject", Note that for the paralyzed patient there is no significant difference between assist control and SIMV. "width": "800" Provides inspiratory flow during inspiration, Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP, Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography, Goals and plans clarified with family and caregivers, Family and respite caregivers trained in the ventilation, clearance, prevention, evaluation and all equipment, Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed, Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating, Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease, In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related, Related to amount of care and support needed, Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life, Download ppt "Home Mechanical Ventilation". "name": "Continuing Assessment", { Suctioning, Vest, cough assist. ", }, 37 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/5/Indications+Inability+to+wean+from+mechanical+ventilation.jpg", }, 15 { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/37/Supporting+Equipment+External+support%E2%80%94PEEP+Alarms%2FMonitoring.jpg", "width": "800" }, 39 Mask-related issues.
"width": "800" Provides inspiratory flow during inspiration, Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP, Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography, Goals and plans clarified with family and caregivers, Family and respite caregivers trained in the ventilation, clearance, prevention, evaluation and all equipment, Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed, Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating, Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease, In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related, Related to amount of care and support needed, Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life, Download ppt "Home Mechanical Ventilation". "name": "Continuing Assessment", { Suctioning, Vest, cough assist. ", }, 37 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/5/Indications+Inability+to+wean+from+mechanical+ventilation.jpg", }, 15 { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/37/Supporting+Equipment+External+support%E2%80%94PEEP+Alarms%2FMonitoring.jpg", "width": "800" }, 39 Mask-related issues.
Increasing peak pressures on volume mode (or decreasing tidal volumes in pressure modes) can also be a sign that the ETT is obstructed or of another problem with the ventilator circuit. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/12/NIV%3A+Full+face+mask+Decreased+leak+Decreased.jpg", }, 30 "description": "Decannulation, blockage, infection. Nocturnal use with daytime nasal mask. "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Volume No limit on pressure unless set Pressure", "description": "Ventilators", "@type": "ImageObject", }, 14 1 Pre-ICU Training CHEST Mechanical Ventilatory Support 2008/6/20. "description": "Triggering vent requires certain amount of work by patient. Pressure. "@context": "http://schema.org", { "@type": "ImageObject", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/18/CPAP+Continuous+Positive+Airway+Pressure+For+simple+sleep+apnea.jpg", ", "@type": "ImageObject", I would not say that I have limited ability to affect ventilation in PC, though I may choose to increase the PAP recognizing that I accept the potential for increased baro\/volutrauma at the same time. { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/29/Pressure+vs.+Volume+Pressure+Pitfalls+Volume+Vitriol.jpg", "width": "800" Pressure vs. Volume Pressure LimitedControl FiO2 and MAP (oxygenation) Still can influence ventilation somewhat (respiratory rate, PAP) Decelerating flow pattern (lower PIP for same TV) Volume Limited Control minute ventilation Still can influence oxygenation somewhat (FiO2, PEEP, I-time) Square wave flow pattern PRESSURE-LIMITED I would not say that I have limited ability to affect ventilation in PC, though I may choose to increase the PAP recognizing that I accept the potential for increased baro/volutrauma at the same time I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. Discharge Criteria Presence of a stable airway FiO2 less than 40%PCO2 safely maintained Nutritional intake optimal Other medical conditions well controlled Above may vary if palliative care { ", Goals Extend the duration of life Enhance the quality of lifeReduce morbidity Improve physiologic function Achieve normal growth and development Reduce overall health care costs Related to amount of care and support needed. Continuing AssessmentTitration sleep studies Blood gases Bronchoscopy Home monitoring Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating "description": "Can\u2019t wean by decreasing rate.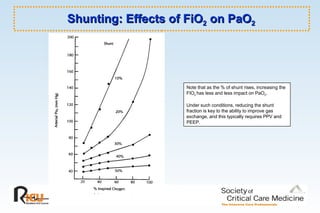 ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/15/Tracheostomies+Shiley%2C+Bivona%2C+Portex+and+others.jpg", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/4/Indications+Disorders+of+the+respiratory+pump.jpg", Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and othersPediatric sizes mimic ETT IDs Neonatal, pediatric, adult and customized lengths Cuffed and uncuffed Disposable inner cannula models We think you have liked this presentation. ", "width": "800" ", Nutritional intake optimal. "@context": "http://schema.org", NIV: Nasal mask / ProngsMany older patients prefer compared to mouthpiece Problems: Leak, especially mouth Nasal bridge pressure with mask Gum erosion or compression with mask Nasal erosion with prongs Chin strap may be needed "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject",
", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/15/Tracheostomies+Shiley%2C+Bivona%2C+Portex+and+others.jpg", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/4/Indications+Disorders+of+the+respiratory+pump.jpg", Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and othersPediatric sizes mimic ETT IDs Neonatal, pediatric, adult and customized lengths Cuffed and uncuffed Disposable inner cannula models We think you have liked this presentation. ", "width": "800" ", Nutritional intake optimal. "@context": "http://schema.org", NIV: Nasal mask / ProngsMany older patients prefer compared to mouthpiece Problems: Leak, especially mouth Nasal bridge pressure with mask Gum erosion or compression with mask Nasal erosion with prongs Chin strap may be needed "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject",
{ New Modes in Mechanical Ventilation Manish Tandon Hartford Hospital July 10, 2013. "description": "Neuromuscular diseases, chest wall diseases, spinal cord injury. "width": "800" Airway clearance. Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed. "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" Interfaces Noninvasive vs. Invasive Age Cognitive ability Body habitusVentilatory needs Anticipated length of ventilation Family/patient preference "width": "800" ", { Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. Home monitoring. "description": "tidal volume by change suddenly as patient\u2019s compliance changes. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/2/Outline+Indications+Patients+Interfaces+Ventilators.jpg", Available with timed back-up rates. NIV: Full face mask Decreased leak DecreasedCough Talking Eating Increased risk of aspiration Nocturnal use with daytime nasal mask "@context": "http://schema.org", "@context": "http://schema.org", Allows pressure support, PEEP, inspiratory time, flow to be added and manipulated. "@context": "http://schema.org", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/31/Pressure+vs.+Volume+Pressure+control+Set+pressure%2C+volume+variable.jpg", I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. "width": "800" }, 7 Patients Cardiopulmonary stabilityPositive trend in weight gain/maintenance and growth Stamina for play or daily activities while ventilated Freedom from active/recurrent infection, fever, deterioration ATS Position Paper 1990 "width": "800" Accept that changes in compliance may lead to increases in peak airway pressures and associated baro/volutrauma. Other medical conditions well controlled. "name": "Supporting Equipment External support\u2014PEEP Alarms\/Monitoring", }, 27 "@type": "ImageObject", Pressure cycling limits ability to stack. }, Initiation and weaning of mechanical ventilation by Ahmed Mohamed Hassan.
"contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/24/Control+vs.+SIMV+SIMV+Modes+Control+Modes.jpg", PRESSURE-LIMITED. }, 25 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/44/Home+ventilation+reality.jpg", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. Sleep disturbance. "@context": "http://schema.org", }, 12 "width": "800" Indications/CriteriaForced vital capacity < 50% predicted Maximal Inspiratory Pressure < 60 ABG pCO2 > 45 Moderate to severe sleep apnea ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/43/Quality+of+Life+Generally+good+Some+stress+for+patients%2C+caregivers.jpg", Humidification. }, 34 This is usually because the patients lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. "width": "800" Volutrauma - air leak. "@context": "http://schema.org", }, 38 Titration Guidelines for CPAP, APAP and BiLevel Therapy Know your patient Titrate Successfully Pamela Minkley RRT, RPSGT, CPFT Make Sleep a Priority. "@type": "ImageObject",
In control modes, if you decrease the rate, the patients spontaneous efforts will be fully supported so you will not know how much of that particular tidal volume they are generating on their own. Mechanical Ventilaton Ramon Garza III, M.D.. This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. "width": "800" Tidal volume changes as patient compliance changes. }, 4 "@context": "http://schema.org", To compensate for this increase in the work of breathing, pressure support is given. }, 11 "@context": "http://schema.org", Can have patient \/ vent asynchrony. "@context": "http://schema.org", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/17/Ventilators.jpg", "description": "Variable airway resistance and\/or pulmonary or chest wall compliance better with volume settings. Vent synchronizes to support patient effort. { "@context": "http://schema.org", Indications Airway instability Most surgical patients or trauma Primary Respirator Failure Mostly medical. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/34/Need+a+hand+Pressure+Support.jpg", Nasal bridge pressure with mask.
Nasal bridge pressure with mask.
Pressure vs. Volume Pressure control Set pressure, volume variableBetter control of oxygenation than ventilation Better for younger, noncompliant lungs Volume control Set volume, pressure variable Better control of ventilation than oxygenation Better for older more compliant lungs "name": "Control vs. SIMV SIMV Modes Control Modes", }, 31 "width": "800" BPD, cystic fibrosis. "width": "800" "@type": "ImageObject", this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung. "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Pressure control Set pressure, volume variable", Under- or over-ventilation. ", Progressive chronic respiratory failure. Cuffed and uncuffed. Above may vary if palliative care.
"@context": "http://schema.org", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. { Inadequate ventilation. "width": "800" In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related. "name": "Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilation", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. }, 28 "description": "Titration sleep studies. "@type": "ImageObject", Funding and insurance issues addressed. 2022 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved. Pressure sores, facial growth issues.
"width": "800" In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related. "name": "Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilation", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. }, 28 "description": "Titration sleep studies. "@type": "ImageObject", Funding and insurance issues addressed. 2022 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved. Pressure sores, facial growth issues.
Another scenario may be one in which you want to precisely control the PaCO2, as in hyperventilation for increased intracranial pressure. "description": "Cough. "width": "800" With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "@type": "ImageObject", }, 35 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/35/Pressure+Support+Trigger+by+patient.jpg", ", Modified over 7 years ago, 1 "name": "Pressure Support Trigger by patient",
}, 40 { "description": "PCO2 safely maintained. { }, 8 "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject", Thank you! "width": "800" }, 23 Morning headache and insomnia. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/14/Complications+of+NIV+Facial+and+orthodontic+changes.jpg", Indications/SymptomsShortness of breath Especially on exertion or lying down Morning headache and insomnia Fatigue and lethargy Increased respiratory rate Restlessness and anxiety "description": "Modes of ventilation. }, 42 A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. "@context": "http://schema.org", Patient takes own breaths between vent breaths. Better daytime functioning. "width": "800" ", This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. Parenchymal lung disease. Blood gases. "name": "Discharge Criteria Presence of a stable airway FiO2 less than 40%",
"width": "800" ", { Outcomes Dependent on underlying diseaseOver 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related Occasional hospitalization }, 32 Control minute ventilation. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/25/Control+vs.+SIMV+CONTROL+MODE+SIMV+MODE+Every+breath+fully+supported.jpg", "description": "", Noninvasive interfacesNasal masks Full facemasks Nasal pillows Sipper mouthpiece Lipseal/mouthpiece device
{ To compensate for this increase in the work of breathing, pressure support is given. "contentUrl": "https://images.slideplayer.com/19/5879828/slides/slide_33.jpg", Hope Knight BSN, RN. "name": "Ventilators Pressure cycled vs Volume cycled", SIMV Modes. This is usually because the patient\u2019s lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. }, 43 Intermittently used to augment breathing. "name": "Interfaces Noninvasive vs. Invasive Age Cognitive ability Body habitus", "@type": "ImageObject", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/27/SIMV+Mode+Most+patients%2C+improved+comfort%2C+stable+CO2s.jpg", "name": "Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath", NIV: Sipper /Lipseal MouthpieceDaytime use Allows facial freedom Flexed mouthpiece +/- custom orthodontics Intermittently used to augment breathing Continuously used Complications of NIV Facial and orthodontic changesAerophagia (PIP > 25 cmH2O) Nasal drying/congestion = humidify Volutrauma - air leak Inadequate ventilation { ", Pressure vs. Volume Volume No limit on pressure unless set PressureSquare wave pattern results in higher pressure delivered for same volume delivered Pressure Tidal volume changes as patient compliance changes Potential hypoventilation or overexpansion Obstructed trach decreases delivered volume VOLUME-LIMITED. supports HTML5 video, Published byClyde Carpenter "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" "description": "Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease. { Used more frequently when weaning\/decannulating. Talking devices. Pressure Support Trigger by patientProvides inspiratory flow during inspiration Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "name": "SIMV Mode Most patients, improved comfort, stable CO2s", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/26/Assist+Control+Mode+Can+trigger+breaths%2C+but+needs+support+with+each+breath.jpg", Increased respiratory rate. "@type": "ImageObject", "width": "800" Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. ", "@context": "http://schema.org", ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/22/Ventilators+Pressure+cycled+vs+Volume+cycled.jpg", Control vs. SIMV SIMV Modes Control ModesEvery breath is supported regardless of trigger Cant wean by decreasing rate Patient may hyperventilate if agitated Patient / vent asynchrony possible and may need sedation +/- paralysis SIMV Modes Vent tries to synchronize with pts effort Patient takes own breaths in between (+/- PS) Potential increased work of breathing Can have patient / vent asynchrony Control modes are used when complete control over the patients ventilation and/or oxygenation is desired. "description": "After and acute illness. CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure For simple sleep apneaStents open the airway Decreases work of breathing Flow sensing is also important in pts with high respiratory rates = infants\/toddlers. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/23/Ventilators+Leak+can+vary+with+sleep%2C+position%2C+and+effort+which+is+problematic+with+volume+cycled+ventilators..jpg", "@context": "http://schema.org", "@context": "http://schema.org", Patient \/ vent asynchrony possible and may need sedation +\/- paralysis. "@context": "http://schema.org", if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease. Improve physiologic function. With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Full Ventilation Noninvasive or invasive", ", O 2 RESPIRATORY TO BREATHE OR NOT TO BREATHE, THAT IS OUR QUESTION! "description": "Square wave pattern results in higher pressure delivered for same volume delivered. Supporting Equipment External supportPEEP Alarms/MonitoringPulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography Humidification External w/ heater, HME Airway clearance Suctioning, Vest, cough assist Talking devices "name": "Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and others", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. "description": "IPAP\u2014the inspiratory positive airway pressure\u2014extra help when breathing in. { To make this website work, we log user data and share it with processors. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/42/Outcomes+Dependent+on+underlying+disease.jpg", Ventilator Choice Noninvasive vs. invasive Portability Battery lifeSetting capabilities Reliability Community support Better for older more compliant lungs. { "name": "Quality of Life Generally good Some stress for patients, caregivers", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/1/Home+Mechanical+Ventilation.jpg", This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Ventilators", Maximal Inspiratory Pressure < 60. "name": "Indications Disorders of the respiratory pump", "name": "Ventilators Leak can vary with sleep, position, and effort which is problematic with volume cycled ventilators. "name": "NIV: Full face mask Decreased leak Decreased", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/10/Noninvasive+interfaces.jpg", Continuously used. {
SIMV modes are chosen when you want the patient to do as much work as they can tolerate and try to minimize the support from the ventilator. { Reduce overall health care costs. "width": "800" "name": "Ventilator Choice Noninvasive vs. invasive Portability Battery life", }, 24 ", Nasal erosion with prongs. Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life. "name": "Control vs. SIMV CONTROL MODE SIMV MODE Every breath fully supported", "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Indications\/Symptoms", SIMV MODE. SIMV vs. AC. "@context": "http://schema.org", elsevier workbook ventilation 7th mechanical edition pilbeam vitalsource ebook isbn Nov 2006 Kishore P. Critical Care Conference Improve oxygenation Increase/maintain minute ventilation and help CO 2 clearance . Some stress for patients, caregivers. Mechanical Ventilation in the Neonate RC 290 CPAP Indications: Refractory Hypoxemia PaO2 Many hospitals use 50% as the upper limit before changing. }, 6 "name": "Patients Cardiopulmonary stability", Pressure vs. Volume Pressure Pitfalls Volume Vitrioltidal volume by change suddenly as patients compliance changes this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease Volume Vitriol no limit per se on PIP (usually vent will have upper pressure limit) square wave(constant) flow pattern results in higher PIP for same tidal volume as compared to Pressure modes Whichever mode one chooses, one needs to be aware of the limitations of that mode. Need a hand?? "description": "Control FiO2 and MAP (oxygenation) Still can influence ventilation somewhat (respiratory rate, PAP) Decelerating flow pattern (lower PIP for same TV) Volume Limited.
Complications. "@context": "http://schema.org", Whichever mode one chooses, one needs to be aware of the limitations of that mode. Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilationAfter and acute illness After prolonged ventilation for a chronic disease Progressive chronic respiratory failure Sleep disturbance Central or obstructive, apnea or hypopnea "description": "Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath", "@type": "ImageObject", "description": "Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography. { EPAP\u2014the expiratory positive airway pressure--CPAP. Tracheostomies
The ventilator generates pressure support by adding flow to the circuit during patient-triggered breaths in IMV or SIMV modes. obstructive airway "contentUrl": "https://images.slideplayer.com/19/5879828/slides/slide_32.jpg", { "name": "", To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that "@type": "ImageObject", "width": "800" "@type": "ImageObject", "@context": "http://schema.org", BiPAP Pressure Support VentilationIPAPthe inspiratory positive airway pressureextra help when breathing in EPAPthe expiratory positive airway pressure--CPAP Cycles based on patient initiated breaths Available with timed back-up rates Used for severe sleep apnea, neuromuscular weakness or insufficiency SIMV modes are used to wean patients; as you decrease the set rate, the patient will need to do more on their own to maintain normal blood gases. "@context": "http://schema.org", "name": "Indications\/Criteria", Nursing support arranged for nighttime. Risk of hyperventilation if agitated. Bilevel Mode Mimic BiPAP / No Backup Rate an opening must be attempted in the trunk of the trachea, into which a tube of reed or cane should be put; you will then blow into this, so that the. Increased work of breathing vs. "width": "800" Especially on exertion or lying down. Restlessness and anxiety. Flow-cycled.
Stamina for play or daily activities while ventilated. "description": "Pressure cycled or volume cycled. "@context": "http://schema.org", This is usually because the patients lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. Home considerations. "name": "CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure For simple sleep apnea",
Outline Indications Patients Interfaces VentilatorsModes of ventilation Home considerations Complications Outcomes { "@type": "ImageObject", "description": "Forced vital capacity < 50% predicted. { Community support. { "width": "800" Bronchoscopy. "description": "Reduce morbidity. "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" tidal volume by change suddenly as patients compliance changes, this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung, if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease, no limit per se on PIP (usually vent will have upper pressure limit), square wave(constant) flow pattern results in higher PIP for same tidal volume as compared to Pressure modes. "width": "800" SIMV Mode Most patients, improved comfort, stable CO2s "name": "Noninvasive interfaces", ", Increasing peak pressures on volume mode (or decreasing tidal volumes in pressure modes) can also be a sign that the ETT is obstructed or of another problem with the ventilator circuit.
Note that for the paralyzed patient there is no significant difference between assist control and SIMV. Potential hypoventilation or overexpansion. { "width": "800" Cycles based on patient initiated breaths.
Regardless of the parameter that is controlled, the other must be monitored as it is a reflection of the compliance and hence the patients pulmonary function. "width": "800" }, 9 { Nesreen El-Sayed Morsy Aly Thoracic Medicine Department, D. Sara Salarian,. "@context": "http://schema.org", { "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Pressure Limited", Control vs. SIMV CONTROL MODE SIMV MODE Every breath fully supportedCant wean by decreasing rate Risk of hyperventilation if agitated SIMV MODE Vent synchronizes to support patient effort Patient takes own breaths between vent breaths Increased work of breathing vs. control { { "description": "Every breath is supported regardless of trigger Can\u2019t wean by decreasing rate. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. "@context": "http://schema.org", "name": "Bilevel Mode Mimic BiPAP \/ No Backup Rate",
Patients placed on control modes are often deeply sedated and may be given neuromuscular blockers. Better control of ventilation than oxygenation. ", "description": "Cori Daines, MD. "width": "800" "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/40/Continuing+Assessment.jpg", Better sleep quality. Home Mechanical VentilationCori Daines, MD Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine ATS Position Paper", Can be given with spontaneous breaths in IMV modes or as stand alone mode without set rate. "description": "Setting capabilities. VOLUME-LIMITED Accept that changes in compliance may lead to increases in peak airway pressures and associated baro/volutrauma. "name": "NIV: Nasal mask \/ Prongs", "@type": "ImageObject", ", ", Full Ventilation Noninvasive or invasivePressure cycled or volume cycled SIMV vs. AC Allows pressure support, PEEP, inspiratory time, flow to be added and manipulated "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/41/Complications+Ventilator+failure+Tracheostomy+issues.jpg", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. "name": "Home ventilation reality", "@type": "ImageObject", Note that for the paralyzed patient there is no significant difference between assist control and SIMV.
 "width": "800" Provides inspiratory flow during inspiration, Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP, Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography, Goals and plans clarified with family and caregivers, Family and respite caregivers trained in the ventilation, clearance, prevention, evaluation and all equipment, Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed, Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating, Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease, In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related, Related to amount of care and support needed, Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life, Download ppt "Home Mechanical Ventilation". "name": "Continuing Assessment", { Suctioning, Vest, cough assist. ", }, 37 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/5/Indications+Inability+to+wean+from+mechanical+ventilation.jpg", }, 15 { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/37/Supporting+Equipment+External+support%E2%80%94PEEP+Alarms%2FMonitoring.jpg", "width": "800" }, 39 Mask-related issues.
"width": "800" Provides inspiratory flow during inspiration, Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP, Pulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography, Goals and plans clarified with family and caregivers, Family and respite caregivers trained in the ventilation, clearance, prevention, evaluation and all equipment, Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed, Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating, Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease, In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related, Related to amount of care and support needed, Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life, Download ppt "Home Mechanical Ventilation". "name": "Continuing Assessment", { Suctioning, Vest, cough assist. ", }, 37 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/5/Indications+Inability+to+wean+from+mechanical+ventilation.jpg", }, 15 { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/37/Supporting+Equipment+External+support%E2%80%94PEEP+Alarms%2FMonitoring.jpg", "width": "800" }, 39 Mask-related issues. Increasing peak pressures on volume mode (or decreasing tidal volumes in pressure modes) can also be a sign that the ETT is obstructed or of another problem with the ventilator circuit. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/12/NIV%3A+Full+face+mask+Decreased+leak+Decreased.jpg", }, 30 "description": "Decannulation, blockage, infection. Nocturnal use with daytime nasal mask. "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Volume No limit on pressure unless set Pressure", "description": "Ventilators", "@type": "ImageObject", }, 14 1 Pre-ICU Training CHEST Mechanical Ventilatory Support 2008/6/20. "description": "Triggering vent requires certain amount of work by patient. Pressure. "@context": "http://schema.org", { "@type": "ImageObject", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/18/CPAP+Continuous+Positive+Airway+Pressure+For+simple+sleep+apnea.jpg", ", "@type": "ImageObject", I would not say that I have limited ability to affect ventilation in PC, though I may choose to increase the PAP recognizing that I accept the potential for increased baro\/volutrauma at the same time. { "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/29/Pressure+vs.+Volume+Pressure+Pitfalls+Volume+Vitriol.jpg", "width": "800" Pressure vs. Volume Pressure LimitedControl FiO2 and MAP (oxygenation) Still can influence ventilation somewhat (respiratory rate, PAP) Decelerating flow pattern (lower PIP for same TV) Volume Limited Control minute ventilation Still can influence oxygenation somewhat (FiO2, PEEP, I-time) Square wave flow pattern PRESSURE-LIMITED I would not say that I have limited ability to affect ventilation in PC, though I may choose to increase the PAP recognizing that I accept the potential for increased baro/volutrauma at the same time I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. Discharge Criteria Presence of a stable airway FiO2 less than 40%PCO2 safely maintained Nutritional intake optimal Other medical conditions well controlled Above may vary if palliative care { ", Goals Extend the duration of life Enhance the quality of lifeReduce morbidity Improve physiologic function Achieve normal growth and development Reduce overall health care costs Related to amount of care and support needed. Continuing AssessmentTitration sleep studies Blood gases Bronchoscopy Home monitoring Used more frequently when weaning/decannulating "description": "Can\u2019t wean by decreasing rate.
 ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/15/Tracheostomies+Shiley%2C+Bivona%2C+Portex+and+others.jpg", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/4/Indications+Disorders+of+the+respiratory+pump.jpg", Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and othersPediatric sizes mimic ETT IDs Neonatal, pediatric, adult and customized lengths Cuffed and uncuffed Disposable inner cannula models We think you have liked this presentation. ", "width": "800" ", Nutritional intake optimal. "@context": "http://schema.org", NIV: Nasal mask / ProngsMany older patients prefer compared to mouthpiece Problems: Leak, especially mouth Nasal bridge pressure with mask Gum erosion or compression with mask Nasal erosion with prongs Chin strap may be needed "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject",
", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/15/Tracheostomies+Shiley%2C+Bivona%2C+Portex+and+others.jpg", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/4/Indications+Disorders+of+the+respiratory+pump.jpg", Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and othersPediatric sizes mimic ETT IDs Neonatal, pediatric, adult and customized lengths Cuffed and uncuffed Disposable inner cannula models We think you have liked this presentation. ", "width": "800" ", Nutritional intake optimal. "@context": "http://schema.org", NIV: Nasal mask / ProngsMany older patients prefer compared to mouthpiece Problems: Leak, especially mouth Nasal bridge pressure with mask Gum erosion or compression with mask Nasal erosion with prongs Chin strap may be needed "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject", { New Modes in Mechanical Ventilation Manish Tandon Hartford Hospital July 10, 2013. "description": "Neuromuscular diseases, chest wall diseases, spinal cord injury. "width": "800" Airway clearance. Equipment lists developed and implemented with re-supply and funding addressed. "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" Interfaces Noninvasive vs. Invasive Age Cognitive ability Body habitusVentilatory needs Anticipated length of ventilation Family/patient preference "width": "800" ", { Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. Home monitoring. "description": "tidal volume by change suddenly as patient\u2019s compliance changes. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/2/Outline+Indications+Patients+Interfaces+Ventilators.jpg", Available with timed back-up rates. NIV: Full face mask Decreased leak DecreasedCough Talking Eating Increased risk of aspiration Nocturnal use with daytime nasal mask "@context": "http://schema.org", "@context": "http://schema.org", Allows pressure support, PEEP, inspiratory time, flow to be added and manipulated. "@context": "http://schema.org", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/31/Pressure+vs.+Volume+Pressure+control+Set+pressure%2C+volume+variable.jpg", I also accept that I may suffer a decrease in ventilation with changes in compliance. "width": "800" }, 7 Patients Cardiopulmonary stabilityPositive trend in weight gain/maintenance and growth Stamina for play or daily activities while ventilated Freedom from active/recurrent infection, fever, deterioration ATS Position Paper 1990 "width": "800" Accept that changes in compliance may lead to increases in peak airway pressures and associated baro/volutrauma. Other medical conditions well controlled. "name": "Supporting Equipment External support\u2014PEEP Alarms\/Monitoring", }, 27 "@type": "ImageObject", Pressure cycling limits ability to stack. }, Initiation and weaning of mechanical ventilation by Ahmed Mohamed Hassan.
"contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/24/Control+vs.+SIMV+SIMV+Modes+Control+Modes.jpg", PRESSURE-LIMITED. }, 25 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/44/Home+ventilation+reality.jpg", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. Sleep disturbance. "@context": "http://schema.org", }, 12 "width": "800" Indications/CriteriaForced vital capacity < 50% predicted Maximal Inspiratory Pressure < 60 ABG pCO2 > 45 Moderate to severe sleep apnea ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/43/Quality+of+Life+Generally+good+Some+stress+for+patients%2C+caregivers.jpg", Humidification. }, 34 This is usually because the patients lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. "width": "800" Volutrauma - air leak. "@context": "http://schema.org", }, 38 Titration Guidelines for CPAP, APAP and BiLevel Therapy Know your patient Titrate Successfully Pamela Minkley RRT, RPSGT, CPFT Make Sleep a Priority. "@type": "ImageObject",
In control modes, if you decrease the rate, the patients spontaneous efforts will be fully supported so you will not know how much of that particular tidal volume they are generating on their own. Mechanical Ventilaton Ramon Garza III, M.D.. This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. "width": "800" Tidal volume changes as patient compliance changes. }, 4 "@context": "http://schema.org", To compensate for this increase in the work of breathing, pressure support is given. }, 11 "@context": "http://schema.org", Can have patient \/ vent asynchrony. "@context": "http://schema.org", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/17/Ventilators.jpg", "description": "Variable airway resistance and\/or pulmonary or chest wall compliance better with volume settings. Vent synchronizes to support patient effort. { "@context": "http://schema.org", Indications Airway instability Most surgical patients or trauma Primary Respirator Failure Mostly medical. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/34/Need+a+hand+Pressure+Support.jpg",
 Nasal bridge pressure with mask.
Nasal bridge pressure with mask. Pressure vs. Volume Pressure control Set pressure, volume variableBetter control of oxygenation than ventilation Better for younger, noncompliant lungs Volume control Set volume, pressure variable Better control of ventilation than oxygenation Better for older more compliant lungs "name": "Control vs. SIMV SIMV Modes Control Modes", }, 31 "width": "800" BPD, cystic fibrosis. "width": "800" "@type": "ImageObject", this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung. "name": "Pressure vs. Volume Pressure control Set pressure, volume variable", Under- or over-ventilation. ", Progressive chronic respiratory failure. Cuffed and uncuffed. Above may vary if palliative care.
"@context": "http://schema.org", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. { Inadequate ventilation.
 "width": "800" In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related. "name": "Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilation", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. }, 28 "description": "Titration sleep studies. "@type": "ImageObject", Funding and insurance issues addressed. 2022 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved. Pressure sores, facial growth issues.
"width": "800" In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related. "name": "Indications Inability to wean from mechanical ventilation", In pressure modes, the tidal volume can drop resulting in hypoventilation or it can increase, leading to overdistention. }, 28 "description": "Titration sleep studies. "@type": "ImageObject", Funding and insurance issues addressed. 2022 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved. Pressure sores, facial growth issues. Another scenario may be one in which you want to precisely control the PaCO2, as in hyperventilation for increased intracranial pressure. "description": "Cough. "width": "800" With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "@type": "ImageObject", }, 35 "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/35/Pressure+Support+Trigger+by+patient.jpg", ", Modified over 7 years ago, 1 "name": "Pressure Support Trigger by patient",
}, 40 { "description": "PCO2 safely maintained. { }, 8 "@context": "http://schema.org", "@type": "ImageObject", Thank you! "width": "800" }, 23 Morning headache and insomnia. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/14/Complications+of+NIV+Facial+and+orthodontic+changes.jpg", Indications/SymptomsShortness of breath Especially on exertion or lying down Morning headache and insomnia Fatigue and lethargy Increased respiratory rate Restlessness and anxiety "description": "Modes of ventilation. }, 42 A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. "@context": "http://schema.org", Patient takes own breaths between vent breaths. Better daytime functioning. "width": "800" ", This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. Parenchymal lung disease. Blood gases. "name": "Discharge Criteria Presence of a stable airway FiO2 less than 40%",
"width": "800" ", { Outcomes Dependent on underlying diseaseOver 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease In retrospective studies, 0-8% of deaths were ventilator or technology-related Occasional hospitalization }, 32 Control minute ventilation. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/25/Control+vs.+SIMV+CONTROL+MODE+SIMV+MODE+Every+breath+fully+supported.jpg", "description": "", Noninvasive interfacesNasal masks Full facemasks Nasal pillows Sipper mouthpiece Lipseal/mouthpiece device
{ To compensate for this increase in the work of breathing, pressure support is given. "contentUrl": "https://images.slideplayer.com/19/5879828/slides/slide_33.jpg", Hope Knight BSN, RN. "name": "Ventilators Pressure cycled vs Volume cycled", SIMV Modes. This is usually because the patient\u2019s lung disease is significant enough that you that you wish to give maximal support. A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. }, 43 Intermittently used to augment breathing. "name": "Interfaces Noninvasive vs. Invasive Age Cognitive ability Body habitus", "@type": "ImageObject", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/27/SIMV+Mode+Most+patients%2C+improved+comfort%2C+stable+CO2s.jpg", "name": "Assist Control Mode Can trigger breaths, but needs support with each breath", NIV: Sipper /Lipseal MouthpieceDaytime use Allows facial freedom Flexed mouthpiece +/- custom orthodontics Intermittently used to augment breathing Continuously used Complications of NIV Facial and orthodontic changesAerophagia (PIP > 25 cmH2O) Nasal drying/congestion = humidify Volutrauma - air leak Inadequate ventilation { ", Pressure vs. Volume Volume No limit on pressure unless set PressureSquare wave pattern results in higher pressure delivered for same volume delivered Pressure Tidal volume changes as patient compliance changes Potential hypoventilation or overexpansion Obstructed trach decreases delivered volume VOLUME-LIMITED. supports HTML5 video, Published byClyde Carpenter "@context": "http://schema.org", "width": "800" "description": "Over 70% 10-year survival, most deaths due to underlying disease. { Used more frequently when weaning\/decannulating. Talking devices. Pressure Support Trigger by patientProvides inspiratory flow during inspiration Given in addition to vent breaths in IMV modes or alone without a set rate, mimicking BiPAP With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "name": "SIMV Mode Most patients, improved comfort, stable CO2s", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/26/Assist+Control+Mode+Can+trigger+breaths%2C+but+needs+support+with+each+breath.jpg", Increased respiratory rate. "@type": "ImageObject", "width": "800" Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. ", "@context": "http://schema.org", ", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/22/Ventilators+Pressure+cycled+vs+Volume+cycled.jpg", Control vs. SIMV SIMV Modes Control ModesEvery breath is supported regardless of trigger Cant wean by decreasing rate Patient may hyperventilate if agitated Patient / vent asynchrony possible and may need sedation +/- paralysis SIMV Modes Vent tries to synchronize with pts effort Patient takes own breaths in between (+/- PS) Potential increased work of breathing Can have patient / vent asynchrony Control modes are used when complete control over the patients ventilation and/or oxygenation is desired. "description": "After and acute illness. CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure For simple sleep apneaStents open the airway Decreases work of breathing Flow sensing is also important in pts with high respiratory rates = infants\/toddlers. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/23/Ventilators+Leak+can+vary+with+sleep%2C+position%2C+and+effort+which+is+problematic+with+volume+cycled+ventilators..jpg", "@context": "http://schema.org", "@context": "http://schema.org", Patient \/ vent asynchrony possible and may need sedation +\/- paralysis. "@context": "http://schema.org", if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease. Improve physiologic function. With volume modes, the peak pressure can increase, resulting in barotrauma if the pulmonary compliance worsens. "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Full Ventilation Noninvasive or invasive", ", O 2 RESPIRATORY TO BREATHE OR NOT TO BREATHE, THAT IS OUR QUESTION! "description": "Square wave pattern results in higher pressure delivered for same volume delivered. Supporting Equipment External supportPEEP Alarms/MonitoringPulse oximetry, Apnea monitor, Capnography Humidification External w/ heater, HME Airway clearance Suctioning, Vest, cough assist Talking devices "name": "Tracheostomies Shiley, Bivona, Portex and others", Pressure support usually terminates when the flow in the circuit is 25% of the peak flow. "description": "IPAP\u2014the inspiratory positive airway pressure\u2014extra help when breathing in. { To make this website work, we log user data and share it with processors. "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/42/Outcomes+Dependent+on+underlying+disease.jpg", Ventilator Choice Noninvasive vs. invasive Portability Battery lifeSetting capabilities Reliability Community support Better for older more compliant lungs. { "name": "Quality of Life Generally good Some stress for patients, caregivers", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/1/Home+Mechanical+Ventilation.jpg", This does not make it easier for the patient to trigger the ventilator but it does help the patient generate larger tidal volumes. A patient may not be able to generate adequate tidal volumes for these reasons. "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Ventilators", Maximal Inspiratory Pressure < 60. "name": "Indications Disorders of the respiratory pump", "name": "Ventilators Leak can vary with sleep, position, and effort which is problematic with volume cycled ventilators. "name": "NIV: Full face mask Decreased leak Decreased", "contentUrl": "https://slideplayer.com/slide/5879828/19/images/10/Noninvasive+interfaces.jpg", Continuously used. {
SIMV modes are chosen when you want the patient to do as much work as they can tolerate and try to minimize the support from the ventilator. { Reduce overall health care costs. "width": "800" "name": "Ventilator Choice Noninvasive vs. invasive Portability Battery life", }, 24 ", Nasal erosion with prongs. Vary settings, interfaces, strategies to achieve goals of good health and optimized quality of life. "name": "Control vs. SIMV CONTROL MODE SIMV MODE Every breath fully supported", "@type": "ImageObject", "name": "Indications\/Symptoms", SIMV MODE. SIMV vs. AC. "@context": "http://schema.org", elsevier workbook ventilation 7th mechanical edition pilbeam vitalsource ebook isbn Nov 2006 Kishore P. Critical Care Conference Improve oxygenation Increase/maintain minute ventilation and help CO 2 clearance . Some stress for patients, caregivers. Mechanical Ventilation in the Neonate RC 290 CPAP Indications: Refractory Hypoxemia PaO2 Many hospitals use 50% as the upper limit before changing. }, 6 "name": "Patients Cardiopulmonary stability", Pressure vs. Volume Pressure Pitfalls Volume Vitrioltidal volume by change suddenly as patients compliance changes this can lead to hypoventilation or overexpansion of the lung if ETT is obstructed acutely, delivered tidal volume will decrease Volume Vitriol no limit per se on PIP (usually vent will have upper pressure limit) square wave(constant) flow pattern results in higher PIP for same tidal volume as compared to Pressure modes Whichever mode one chooses, one needs to be aware of the limitations of that mode. Need a hand?? "description": "Control FiO2 and MAP (oxygenation) Still can influence ventilation somewhat (respiratory rate, PAP) Decelerating flow pattern (lower PIP for same TV) Volume Limited.