An introduction to time series analysis in the time domain and spectral domain. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT2 after completing STATW21, STAT20, STAT21, STAT 25, STAT S2, STAT 21X, STAT N21, STAT 5, or STAT 2X. STAT133 recommended, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018 The topics of this course change each semester, and multiple sections may be offered. Advanced Topics in Learning and Decision Making: Terms offered: Spring 2011, Spring 2010, Spring 2009, Introduction to Modern Biostatistical Theory and Practice, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Fall 2019, , asymptotic linearity/normality, the delta method, bootstrapping, machine learning, targeted maximum likelihood estimation. This course will focus on approaches to causal inference using the potential outcomes framework. Students engage in professionally-oriented group research under the supervision of a research advisor.
Markov decision processes and partially observable Markov decision processes. The R statistical language is used. Effects of departures from the underlying assumptions. The courses are primarily intended for graduate students and advanced undergraduate students from the mathematical sciences. The course is designed primarily for those who are already familiar with programming in another language, such as python, and want to understand how R works, and for those who already know the basics of R programming and want to gain a more in-depth understanding of the language in order to improve their coding. Normal approximation. Game Theory: Read More [+], Summer: 8 weeks - 6 hours of lecture per week, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020 Recent topics include: Graphical models and approximate inference algorithms. Individual study in consultation with the graduate adviser, intended to provide an opportunity for qualified students to prepare themselves for the master's comprehensive examinations. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 200A after completing Statistics 201A-201B. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Grading/Final exam status: The grading option will be decided by the instructor when the class is offered. Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-36 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 4-45 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 3-36 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 2.5-27 hours of independent study per week, Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Classification regression, clustering, dimensionality, reduction, and density estimation. This course and Pb Hlth C240C/Stat C245C provide an introduction to computational statistics with emphasis on statistical methods and software for addressing high-dimensional inference problems that arise in current biological and medical research.
The second course is Statistics C245F/Public Health C240F. Knowledge of scientific computing environment (R or Matlab) often required. The R statistical language is used. Bayesian methods and concepts: conditional probability, one-parameter and multiparameter models, prior distributions, hierarchical and multi-level models, predictive checking and sensitivity analysis, model selection, linear and generalized linear models, multiple testing and high-dimensional data, mixtures, non-parametric methods. Reproducible and Collaborative Statistical Data Science: Terms offered: Spring 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2010, Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Spring 2017, Supervised Independent Study and Research, Terms offered: Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Spring 2017. Statistical Models: Theory and Application: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 215A or consent of instructor, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020 Examples of possible topics include planning and design of experiments, ANOVA and random effects models, splines, classification, spatial statistics, categorical data analysis, survival analysis, and multivariate analysis. Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018, Modern Statistical Prediction and Machine Learning. Share an intellectual experience with faculty and students by reading "Interior Chinatown" over the summer, attending author Charles Yu's live event on August 26, signing up for L&S 10: The On the Same Page Course, and participating in fall program activities. Introduction to Advanced Programming in R. , and object systems. Topics include: probability, conditioning, and independence; random variables; distributions and joint distributions; expectation, variance, tail bounds; Central Limit Theorem; symmetries in random permutations; prior and posterior distributions; probabilistic models; bias-variance tradeoff; testing hypotheses; correlation and the regression model. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 200A-200B after completing Statistics 201A-201B. The course and lab include hands-on experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Descriptive statistics, probability models and related concepts, sample surveys, estimates, confidence intervals, tests of significance, controlled experiments vs. observational studies, correlation and regression. Experience with R is assumed. Possible topics include: analysis of qualitative/categorical data; loglinear models and latent-structure analysis; the analysis of cross-classified data having ordered and unordered categories; measure, models, and graphical displays in the analysis of cross-classified data; correspondence analysis, association analysis, and related methods of data analysis. The Berkeley Seminar Program has been designed to provide new students with the opportunity to explore an intellectual topic with a faculty member in a small-seminar setting. Approaches to causal inference using the potential outcomes framework. Most time is spent on 2 approaches: mixed models based upon explicit (latent variable) maximum likelihood estimation of the sources of the dependence, versus empirical estimating equation approaches (generalized estimating equations). Final exam not required. Topics include group comparisons and ANOVA, standard parametric statistical models, multivariate data visualization, multiple linear regression, logistic regression and classification, regression trees and random forests. Characteristic function methods. Statistics 135 may be taken concurrently. Reinforcement learning.  Societal Risks and the Law: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture and 1 hour of discussion per week. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STATC140 after completing STAT134. Grading: Letter grade. As a member of the UC Berkeley community, I act with honesty, integrity, and respect for others.. Statistical Computing: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Knowledge of a higher level programming language, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Fall 2019 Principles & Techniques of Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: COMPSCIC8 / DATAC8 / INFOC8 / STATC8; and COMPSCI61A, COMPSCI 88, or ENGIN7; Corequisite: MATH54 or EECS16A. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture per week, Summer: 8 weeks - 7.5 hours of lecture per week, Introductory Probability and Statistics for Business: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Summer 2021 8 Week Session, Summer 2020 8 Week Session, Summer 2019 8 Week Session The Statistics of Causal Inference in the Social Science. Foundations of data science from three perspectives: inferential thinking, computational thinking, and real-world relevance. Introduction to Modern Biostatistical Theory and Practice: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 200A (may be taken concurrently), Introduction to Modern Biostatistical Theory and Practice: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019 Introduction to Probability and Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read More [+]. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT201A after completing STAT200A. Interval estimation. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC200\COMPSCIC200A\STATC200C after completing DATAC100. Individual Study for Master's Candidates: Read More [+]. Covers observational studies with and without ignorable treatment assignment, randomized experiments with and without noncompliance, instrumental variables, regression discontinuity, sensitivity analysis and randomization inference. frame data science questions relevant to longitudinal studies as the estimation of statistical parameters generated from regression, A coordinated treatment of linear and generalized linear models and their application. Principles and Techniques of Data Science: Introduction to Probability at an Advanced Level. Individual Study for Doctoral Candidates: Read More [+], Prerequisites: One year of full-time graduate study and permission of the graduate adviser. Longitudinal Data Analysis: Read More [+], Course Objectives: After successfully completing the course, you will be able to: Stochastic Processes: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics W21 after completing Statistics 2, 20, 21, N21 or 25. Introduction to Probability at an Advanced Level: Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level. Measure theory concepts needed for probability. Some standard significance tests. This course prepares students for data analysis with R. The focus is on the computational model that underlies the R language with the goal of providing a foundation for coding. Stochastic Analysis with Applications to Mathematical Finance, Terms offered: Spring 2008, Spring 2006, Spring 2005. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. Grading: The grading option will be decided by the instructor when the class is offered. The course is designed as a sequence with with Statistics C205A/Mathematics C218A with the following combined syllabus. Comprehension of broad concepts is the main goal, but practical implementation in R is also emphasized. Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 Course covers statistical issues surrounding estimation of effects using data on units followed through time. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture, 2 hours of discussion, and 1 hour of supplement per week, Probability for Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Genomics is one of the fundamental areas of research in the biological sciences and is rapidly becoming one of the most important application areas in statistics. experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Graduate standing and appointment as a graduate student instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Professional course for teachers or prospective teachers, Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2020, Spring 2020. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021. Experience with R is assumed. An introduction to computationally intensive applied statistics. Central limit theorem. Non-linear optimization with applications to statistical procedures. Supervised Independent Study and Research: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 1-4 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week, Supervised Independent Study and Research: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2018, Fall 2011, Fall 2010 Join the online learning revolution! Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of web-based lecture per week, Summer: 8 weeks - 7.5 hours of web-based lecture per week, Terms offered: Spring 2021, Fall 2016, Fall 2003 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC8\COMPSCIC8\INFOC8\STATC8 after completing COMPSCI 8, or DATA 8. Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read More [+], Prerequisites: STAT 102 or STAT135. Corequisite: Mathematics 54, Electrical Engineering 16A, Statistics 89A, Mathematics 110 or equivalent linear algebra.
Societal Risks and the Law: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture and 1 hour of discussion per week. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STATC140 after completing STAT134. Grading: Letter grade. As a member of the UC Berkeley community, I act with honesty, integrity, and respect for others.. Statistical Computing: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Knowledge of a higher level programming language, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Fall 2019 Principles & Techniques of Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: COMPSCIC8 / DATAC8 / INFOC8 / STATC8; and COMPSCI61A, COMPSCI 88, or ENGIN7; Corequisite: MATH54 or EECS16A. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture per week, Summer: 8 weeks - 7.5 hours of lecture per week, Introductory Probability and Statistics for Business: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Summer 2021 8 Week Session, Summer 2020 8 Week Session, Summer 2019 8 Week Session The Statistics of Causal Inference in the Social Science. Foundations of data science from three perspectives: inferential thinking, computational thinking, and real-world relevance. Introduction to Modern Biostatistical Theory and Practice: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 200A (may be taken concurrently), Introduction to Modern Biostatistical Theory and Practice: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019 Introduction to Probability and Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read More [+]. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT201A after completing STAT200A. Interval estimation. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC200\COMPSCIC200A\STATC200C after completing DATAC100. Individual Study for Master's Candidates: Read More [+]. Covers observational studies with and without ignorable treatment assignment, randomized experiments with and without noncompliance, instrumental variables, regression discontinuity, sensitivity analysis and randomization inference. frame data science questions relevant to longitudinal studies as the estimation of statistical parameters generated from regression, A coordinated treatment of linear and generalized linear models and their application. Principles and Techniques of Data Science: Introduction to Probability at an Advanced Level. Individual Study for Doctoral Candidates: Read More [+], Prerequisites: One year of full-time graduate study and permission of the graduate adviser. Longitudinal Data Analysis: Read More [+], Course Objectives: After successfully completing the course, you will be able to: Stochastic Processes: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics W21 after completing Statistics 2, 20, 21, N21 or 25. Introduction to Probability at an Advanced Level: Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level. Measure theory concepts needed for probability. Some standard significance tests. This course prepares students for data analysis with R. The focus is on the computational model that underlies the R language with the goal of providing a foundation for coding. Stochastic Analysis with Applications to Mathematical Finance, Terms offered: Spring 2008, Spring 2006, Spring 2005. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. Grading: The grading option will be decided by the instructor when the class is offered. The course is designed as a sequence with with Statistics C205A/Mathematics C218A with the following combined syllabus. Comprehension of broad concepts is the main goal, but practical implementation in R is also emphasized. Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 Course covers statistical issues surrounding estimation of effects using data on units followed through time. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture, 2 hours of discussion, and 1 hour of supplement per week, Probability for Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Genomics is one of the fundamental areas of research in the biological sciences and is rapidly becoming one of the most important application areas in statistics. experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Graduate standing and appointment as a graduate student instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Professional course for teachers or prospective teachers, Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2020, Spring 2020. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021. Experience with R is assumed. An introduction to computationally intensive applied statistics. Central limit theorem. Non-linear optimization with applications to statistical procedures. Supervised Independent Study and Research: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 1-4 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 1-3 hours of independent study per week, Supervised Independent Study and Research: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2018, Fall 2011, Fall 2010 Join the online learning revolution! Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of web-based lecture per week, Summer: 8 weeks - 7.5 hours of web-based lecture per week, Terms offered: Spring 2021, Fall 2016, Fall 2003 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC8\COMPSCIC8\INFOC8\STATC8 after completing COMPSCI 8, or DATA 8. Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read More [+], Prerequisites: STAT 102 or STAT135. Corequisite: Mathematics 54, Electrical Engineering 16A, Statistics 89A, Mathematics 110 or equivalent linear algebra.
Introduction to Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Mathematics 1A, Mathematics 16A, Mathematics 10A/10B, or consent of instructor. Recent topics include: Bayesian statistics, statistics and finance, random matrix theory, high-dimensional statistics. Prerequisites might vary with instructor and topics. Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2019, Spring 2017, Spring 2015 A deficient grade in STAT21 may be removed by taking STAT20, STATW21, or STAT N21. Computing techniques, numerical methods, simulation and general implementation of biostatistical analysis techniques with emphasis on data applications. This will create time for a unit on the convergence and reversibility of Markov Chains as well as added focus on conditioning and Bayes methods.With about a thousand students a year taking Foundations of Data Science (Stat/CS/Info C8, a.k.a. Further topics such as: continuous time Markov chains, queueing theory, point processes, branching processes, renewal theory, stationary processes, Gaussian processes. This course provides an introduction to computational statistics, with emphasis on statistical methods and software for addressing high-dimensional inference problems in biology and medicine. Corequisites: MATH54 or EECS16A. Linear regression and generalizations (e.g., GLMs, ridge regression, lasso). Model formulation, fitting, and validation and testing. Selected topics such as the Poisson process, Markov chains, characteristic functions. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022 Preparatory Statistics: Read More [+], Summer: 6 weeks - 5 hours of lecture and 4.5 hours of workshop per week8 weeks - 5 hours of lecture and 4.5 hours of workshop per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Undergraduate. Terms offered: Summer 2016 10 Week Session, Summer 2015 10 Week Session, Summer 2014 10 Week Session, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Summer 2021 8 Week Session, Fall 2020. of real-world datasets, including economic data, document collections, geographical data, and social networks. Freshman and sophomore seminars offer lower division students the opportunity to explore an intellectual topic with a faculty member and a group of peers in a small-seminar setting. Algorithms in statistical computing: random number generation, generating other distributions, random sampling and permutations. Statistical Learning Theory: Read More [+], Instructors: Bartlett, Jordan, Wainwright, Statistical Learning Theory: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2017, Spring 2016 Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 0.5-8 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 1.5-20 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 1-15 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 1-12 hours of independent study per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Graduate examination preparation, Individual Study for Master's Candidates: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 The essentials of stochastic analysis, particularly those most relevant to financial engineering, will be surveyed: Brownian motion, stochastic integrals, Ito's formula, representation of martingales, Girsanov's theorem, stochastic differential equations, and diffusion processes. Conditional expectations, martingales and martingale convergence theorems. Units may not be used to meet either unit or residence requirements for a master's degree. Convergence, Markov chains. A deficient grade in DATAC102 may be removed by taking STAT 102, STAT 102, or DATA 102.
Special tutorial or seminar on selected topics. Advanced topics in probability offered according to students demand and faculty availability. Operate effectively in a UNIX environment and on remote servers. Repeat rules: Course may be repeated for credit with instructor consent. If you just want to print information on specific tabs, you're better off downloading a PDF of the page, opening it, and then selecting the pages you really want to print. Primary focus is from the analysis side. Probability Theory: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2020, Fall 2016, Fall 2015, Fall 2014 Applications are drawn from a variety of fields including political science, economics, sociology, public health and medicine. Data, Inference, and Decisions: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Mathematics 54 or Mathematics 110 or Statistics 89A or Physics 89 or both of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 16A and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 16B; Statistics/Computer Science C100; and any of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 126, Statistics 140, Statistics 134, Industrial Engineering and Operations Research 172. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture and 2 hours of discussion per week, Summer: 8 weeks - 6 hours of lecture and 4 hours of discussion per week, Probability and Mathematical Statistics in Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020 A course in algorithms and knowledge of at least one computing language (e.g., R, matlab) is recommended, Instructors: Dudoit, Huang, Nielsen, Song, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2018, Spring 2017 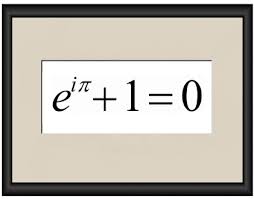 Properties of various estimators including ratio, regression, and difference estimators. Sampling with unequal probabilities. Contemporary methods as extensions of classical methods. This course teaches a broad range of statistical methods that are used to solve data problems. Data 8), there is considerable demand for follow-on courses that build on the skills acquired in that class. Conditional expectation, independence, laws of large numbers.
Properties of various estimators including ratio, regression, and difference estimators. Sampling with unequal probabilities. Contemporary methods as extensions of classical methods. This course teaches a broad range of statistical methods that are used to solve data problems. Data 8), there is considerable demand for follow-on courses that build on the skills acquired in that class. Conditional expectation, independence, laws of large numbers.
Understand in depth and make use of principles of numerical linear algebra, optimization, and simulation for statistics-related research. Introductory Probability and Statistics for Business: Read More [+].
Randomization, blocking, factorial design, confounding, fractional replication, response surface methodology, optimal design. It will also use causal diagrams at an intuitive level. So Stat 140 will start faster than Stat 134 (due to the Data 8 prerequisite), avoid approximations that are unnecessary when SciPy is at hand, and replace some of the routine calculus by symbolic math done in SymPy. Distributions in probability and statistics, central limit theorem, Poisson processes, modes of convergence, transformations involving random variables.
Corequisite or Prerequisite: Foundations of Data Science (COMPSCIC8 / DATAC8 / INFOC8 / STATC8). Tools for reading, analyzing, and plotting data are covered, such as data input/output, reshaping data, the formula language, and graphics models. Individual and/or group meetings with faculty. Statistical Models: Theory and Application: Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2018, Spring 2013. for Bayesian methods and decision theory. Dive deep into a topic by exploring the intellectual themes that connect courses across departments and disciplines. Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Mathematics 53-54, Statistics 134, 135. Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Individual Study for Master's Candidates: Individual Study for Doctoral Candidates: Berkeley Berkeley Academic Guide: Academic Guide 2022-23.
Measure theory concepts needed for probability. Two and higher way layouts, residual analysis. Societal Risks and the Law: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022  Emphasis on experience with real data and assessing statistical assumptions.
Emphasis on experience with real data and assessing statistical assumptions.
Brownian motion. Probability and Mathematical Statistics in Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Prerequisite: one semester of calculus at the level of Math 16A, Math 10A, or Math 1A. A deficient grade in STAT33A may be removed by taking STAT33B, or STAT133. Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018. is modeled appropriately. Probability spaces, random variables, distributions in probability and statistics, central limit theorem, Poisson processes, transformations involving random variables, estimation, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, linear models, large sample theory, categorical models, decision theory. It delves into social and legal issues surrounding data analysis, including issues of privacy and data ownership. Course emphasizes a regression model approach for estimating associations of disease incidence modeling, continuous outcome data/linear models & longitudinal extensions to nonlinear models forms (e.g., logistic). Course builds on 215A in developing critical thinking skills and the techniques of advanced applied statistics. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 204 after completing Statistics 205A-205B. Topics include marginal estimation of a survival function, estimation of a generalized multivariate linear regression model (allowing missing covariates and/or outcomes), estimation of a multiplicative intensity model (such as Cox proportional hazards model) and estimation of causal parameters assuming marginal structural models. This course develops the probabilistic foundations of inference in data science, and builds a comprehensive view of the modeling and decision-making life cycle in data science including its human, social, and ethical implications. Topics include statistical decision theory; point estimation; minimax and admissibility; Bayesian methods; exponential families; hypothesis testing; confidence intervals; small and large sample theory; and M-estimation. Stochastic Analysis with Applications to Mathematical Finance: Quantitative/Statistical Research Methods in Social Sciences, Terms offered: Spring 2016, Spring 2015, Spring 2014. parran evc math epi The goal of this course is to better understand programming principles in general and to write better R code that capitalizes on the language's design. Basic theory for Bayesian methods and decision theory.  Statistics 133 is recommended, The Design and Analysis of Experiments: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Fall 2018 A seminar on successful research designs and a forum for students to discuss the research methods needed in their own work, supplemented by lectures on relevant statistical and computational topics such as matching methods, instrumental variables, regression discontinuity, and Bayesian, maximum likelihood and robust estimation. Markov chains. zhu ying ucsd edu Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Formerly known as: 216A-216B and 217A-217B, Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2016 Typical topics have been model selection; empirical and point processes; the bootstrap, stochastic search, and Monte Carlo integration; information theory and statistics; semi- and non-parametric modeling; time series and survival analysis. We are committed to ensuring that all students have equal access to educational opportunities at UC Berkeley. Brownian motion.
Statistics 133 is recommended, The Design and Analysis of Experiments: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Fall 2018 A seminar on successful research designs and a forum for students to discuss the research methods needed in their own work, supplemented by lectures on relevant statistical and computational topics such as matching methods, instrumental variables, regression discontinuity, and Bayesian, maximum likelihood and robust estimation. Markov chains. zhu ying ucsd edu Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Formerly known as: 216A-216B and 217A-217B, Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2016 Typical topics have been model selection; empirical and point processes; the bootstrap, stochastic search, and Monte Carlo integration; information theory and statistics; semi- and non-parametric modeling; time series and survival analysis. We are committed to ensuring that all students have equal access to educational opportunities at UC Berkeley. Brownian motion.