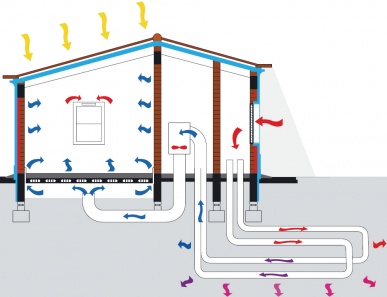
One of the most useful post-construction evaluation tools has been the use of thermography using digital thermal imaging cameras for a formal quantitative scientific energy audit. Window sections should be adequately sized, and to avoid over-illumination can be shielded with a Brise soleil, awnings, well placed trees, glass coatings, and other passive and active devices.[31]. It absorbs almost all the radiation in the visible portion of the solar spectrum and emits very little in the infrared range. A passive solar house requires careful design and siting, which vary by local climate conditions. Passive solar building design is often a foundational element of a cost-effective zero energy building. Mechanical ventilation is one way of bringing in cool air at night, but convective cooling is another option. Vented thermal storage walls vented to the interior have proven somewhat ineffective, mostly because they deliver too much heat during the day in mild weather and during summer months; they simply overheat and create comfort issues. Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable EnergyForrestal Building1000 Independence Avenue, SWWashington, DC 20585. window coverings or movable window insulation. An extension of the "passive solar" approach to seasonal solar capture and storage of heat and cooling. [5], The economic motivation for scientific design and engineering is significant. cooling or, Obstructions / Over-shadowing to solar gain or local cross-winds. The simplest rule of thumb is that thermal mass area should have an area of 5 to 10 times the surface area of the direct-gain collector (glass) area.[20]. The effectiveness of direct solar gain systems is significantly enhanced by insulative (e.g. [43], Architectural engineering that uses the Sun's heat without electric or mechanical systems, Site specific considerations during design, Design elements for residential buildings in temperate climates, Efficiency and economics of passive solar heating, Key passive solar building configurations, Special glazing systems and window coverings, Comparison to the Passive House standard in Europe. A design with too much equator-facing glass can result in excessive winter, spring, or fall day heating, uncomfortably bright living spaces at certain times of the year, and excessive heat transfer on winter nights and summer days. A cool roof, or green roof in addition to a radiant barrier can help prevent your attic from becoming hotter than the peak summer outdoor air temperature[13] (see albedo, absorptivity, emissivity, and reflectivity). gain passive solar direct systems If youre remodeling an existing home, the first step is to have ahome energy auditto prioritize the most cost-effective energy efficiency improvements. [citation needed]. Brian Norton (2011) Solar Water Heaters: A Review of Systems Research and Design Innovation, Green. Kachadorian demonstrated that the drawbacks of thermal storage walls can be overcome by orienting the Trombe wall horizontally instead of vertically. earth heat cooling tube air system heating exchangers tubes solar exchanger passive aircrete geothermal thermal designing energy designingbuildings systems sand Vents must be closed at night so radiant heat from the interior surface of the storage wall heats the indoor space. As the glass tilts off the vertical axis, however, an increased area (now the sloped cross-section) of the glazing has to bear the force of gravity. Much has been learned about passive solar building design since the 1970s energy crisis. It is possible to have active solar hot water which is also capable of being "off grid" and qualifies as sustainable. The Kachadorian floor design is a direct-gain passive solar system, but its thermal mass also acts as an indirect heating (or cooling) element, giving up its heat at night. The thermal mass also tempers the intensity of the heat during the day by absorbing energy. There is no such thing as a "one-size-fits-all" universal passive solar building design that would work well in all locations. Factors that can degrade thermal performance: Technically, PSH is highly efficient. A well-designed overhang may be all that is necessary to shade the glazing in the summer. Western and eastern sun can provide warmth and lighting, but are vulnerable to overheating in summer if not shaded. This should be based on the net glass or glazing area. If it had been applied comprehensively to new building construction beginning in 1980 (based on 1970s lessons learned), America could be saving over $250,000,000 per year on expensive energy and related pollution today. The climate determines the best natural ventilation strategy. Skylights provide daylight. Careful arrangement of rooms completes the passive solar design. A roof pond passive solar system, sometimes called a solar roof, uses water stored on the roof to temper hot and cold internal temperatures, usually in desert environments. The amount of radiant heat received is related to the location latitude, altitude, cloud cover, and seasonal / hourly angle of incidence (see Sun path and Lambert's cosine law). Other creative solutions involve the use of reflecting surfaces to admit daylight into the interior of a building. Experienced passive solar home designers plan for summer comfort as well as winter heating. A thermal storage wall typically consists of a 4 to 16 in (100 to 400mm) thick masonry wall coated with a dark, heat-absorbing finish (or a selective surface) and covered with a single or double layer of high transmissivity glass. Various methods can be employed to address this including but not limited to window coverings, insulated glazing and novel materials such as aerogel semi-transparent insulation, optical fiber embedded in walls or roof, or hybrid solar lighting at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. A reasonable way to analyse these systems is by measuring their coefficient of performance. This will then radiate heat into the building in the evening. Some systems enlist small fans or solar-heated chimneys to improve convective air-flow. You can partially reduce some of the unwanted roof-angled-glazing summer solar heat gain by installing a skylight in the shade of deciduous (leaf-shedding) trees, or by adding a movable insulated opaque window covering on the inside or outside of the skylight. A sunspace with a masonry thermal wall will need approximately 0.3ft2 of thermal mass wall surface per ft2 of floor area being heated (0.3 m2 per m2 of floor area), depending on climate. convert into "useful" heat) 6570% of the energy of solar radiation that strikes the aperture or collector. Alternatively, passive solar computer software can determine the impact of sun path, and cooling-and-heating degree days on energy performance. For winter solar gain it is desirable to use deciduous plants that drop their leaves in the autumn gives year round passive solar benefits. Landscapingcan also help keep your passive solar home comfortable during the cooling season. The most common indirect gain systems is a Trombe wall. With the angles of incidence of sunlight during the day, roof ponds are only effective for heating at lower and mid-latitudes, in hot to temperate climates.
However, unlike masonry water requires carefully designed structural support, and thus it is more difficult to integrate into the design of the house. In equatorial regions at less than 23.5 degrees, the position of the sun at solar noon will oscillate from north to south and back again during the year. The performance of Trombe walls is diminished if the wall interior is not open to the interior spaces. There are three distinct passive solar energy configurations,[20] and at least one noteworthy hybrid of these basic configurations: In a direct-gain passive solar system, the indoor space acts as a solar collector, heat absorber, and distribution system. The oldest and simplest form of convective cooling is designed to bring in cool night air from the outside and push out hot interior air. "Sawtooth roof glazing" with vertical-glass-only can bring some of the passive solar building design benefits into the core of a commercial or industrial building, without the need for any roof-angled glass or skylights. Before you add solar features to your new home design or existing house, remember that energy efficiency is the most cost-effective strategy for reducing heating and cooling bills. It is an alternating cycle hybrid energy system, like a hybrid electric vehicle. When sunlight strikes a building, the building materials can reflect, transmit, or absorb the solar radiation. One is an attached south facing sunroom that is vented at the top. Additional south-facing glazing can be included only if more thermal mass is added. Erecting correctly sized, latitude-specific roof overhangs, Deviation from ideal orientation and northsouth/east/west aspect ratio, Excessive glass area ("over-glazing") resulting in overheating (also resulting in glare and fading of soft furnishings) and heat loss when ambient air temperatures fall, Installing glazing where solar gain during the day and thermal losses during the night cannot be controlled easily e.g. In traditional Japanese architecture the Shji sliding panel doors, with translucent Washi screens, are an original precedent. Although the position of a thermal storage wall minimizes daytime overheating of the indoor space, a well-insulated building should be limited to approximately 0.2 to 0.3ft2 of thermal mass wall surface per ft2 of floor area being heated (0.2 to 0.3 m2 per m2 of floor area), depending upon climate. Williams Sustainable Growers gets planting! Indirect-gain and isolated-gain configurations may still be able to function effectively with only single-pane glazing. Passive solar fraction (PSF) is the percentage of the required heat load met by PSH and hence represents potential reduction in heating costs. The sun is low on the horizon during sunrise and sunset, so overhangs on east and west facing windows are not as effective. The requirement for vertical equator-facing glass is different from the other three sides of a building. In Northern Hemisphere non-tropical latitudes farther than 23.5 degrees from the equator: The converse is observed in the Southern Hemisphere, but the sun rises to the east and sets toward the west regardless of which hemisphere you are in. The zero heating building reduces on the passive solar design and makes the building more opened to conventional architectural design. West-facing, angled glazing, skylights, Thermal losses through non-insulated or unprotected glazing, Lack of adequate shading during seasonal periods of high solar gain (especially on the West wall), Open staircases leading to unequal distribution of warm air between upper and lower floors as warm air rises, High building surface area to volume Too many corners, This page was last edited on 29 June 2022, at 12:43. Such a green facade, or vegetation covering the outer walls, can combat the usage of air conditioning greatly - as much as 80%, as discovered by the researchers. Nighttime thermal losses through the thermal mass of the wall can still be significant in cloudy and cold climates; the wall loses stored heat in less than a day, and then leak heat, which dramatically raises backup heating requirements. Many unscientific, intuition-based expensive construction experiments have attempted and failed to achieve zero energy the total elimination of heating-and-cooling energy bills. Williams College achieves STARS Gold sustainability rating. In cold climates, double glazing should be used to reduce conductive losses through the glass to the outside. Heat transfer in buildings occurs through convection, conduction, and thermal radiation through roof, walls, floor and windows.[10].
Solar heat migrates through the wall, reaching its rear surface in the late afternoon or early evening. Movable shutters, shades, shade screens, or window quilts can accommodate day-to-day and hour-to-hour solar gain and insulation requirements. Glass framing is typically metal (e.g., aluminum) because vinyl will soften and wood will become super dried at the 180F (82C) temperature that can exist behind the glass in the wall. Solar heat gain through windows can be reduced by insulated glazing, shading, and orientation. For occupant safety, regulatory agencies usually require sloped glass to be made of safety glass, laminated, or a combination thereof, which reduce solar gain potential. Thermal mass can include a masonry floor, a masonry wall bordering the house, or water containers. The complex interaction of thermodynamic principles can be counterintuitive for first-time designers. Night-time heat loss, although significant during winter months, is not as essential in the sunspace as with direct gain systems since the sunspace can be closed off from the rest of the building.